Some counseling to learn more about lithium-ion batteries
2022-11-08
Batteries are divided into primary batteries, which can be used only once, and secondary batteries, which can be recharged multiple times. Lithium-ion batteries are secondary batteries that can be recharged. Compared with other types of batteries, they are not only small and lightweight, but also can store more electric energy.
1. How lithium-ion batteries work to generate electricity
There are all kinds of batteries besides lithium-ion, and they all actually work the same basic way to generate electricity. A battery has a positive electrode (positive electrode) and a negative electrode (negative electrode) using a metal material, and a material (electrolyte) that conducts electricity by means of ions is filled between the positive and negative electrodes. A metal electrode is melted by an electrolyte and divided into ions and electrons, which move from a negative to a positive electrode to generate an electric current. A secondary battery generates electricity by charging electrons in the negative terminal before using the battery, and then moving the electrons to the positive terminal.
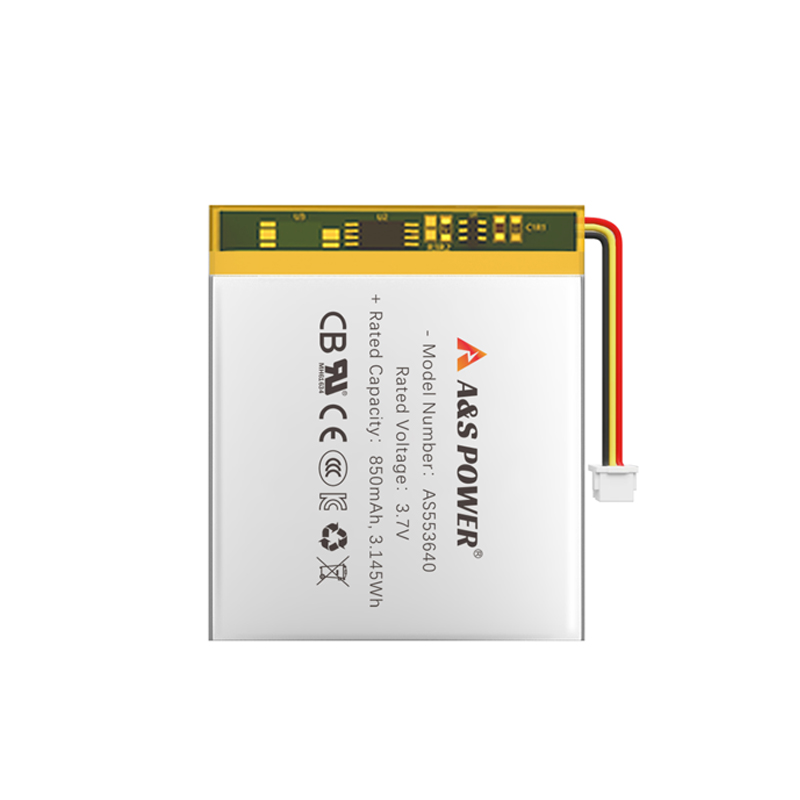
Lithium-ion batteries are predisposed to use lithium-containing metal compounds in the positive terminal and carbon (graphite), which can absorb lithium, in the negative terminal. This allows electricity to be generated without the need for electrolytes to melt the electrodes, as in conventional batteries. This slows the ageing of the battery itself, saving more power and allowing it to be charged and discharged more often. In addition, lithium is very small and light, which makes batteries small and lightweight, among other advantages.
2. Are there different kinds of lithium-ion batteries?
There are several types of lithium-ion batteries, depending on the metal used for the positive electrode. The original lithium-ion batteries used cobalt as a metal for the positive electrode. But cobalt, which is produced in almost as small quantities as lithium, is a rare metal and expensive to make. Hence the use of cheap materials with low environmental load, such as manganese, nickel, iron and other metals. Lithium ion batteries are classified by the materials they are used in. Here's a look at the characteristics of each class.
Cobalt lithium ion battery
Lithium cobalt oxide is used for the positive electrode. Lithium cobaltate is easy to synthesize and easy to use, so the earliest mass-produced lithium-ion battery is lithium cobaltate battery. But because cobalt is a rare metal and expensive, it is hardly used in car parts.
Manganese lithium ion battery
Lithium manganate is used for the positive electrode. The advantage is that the voltage can be similar to that of cobalt-based lithium-ion batteries, and they are cheap to make. The disadvantage is that manganese may melt into the electrolyte during charging and discharging, shortening the battery life.
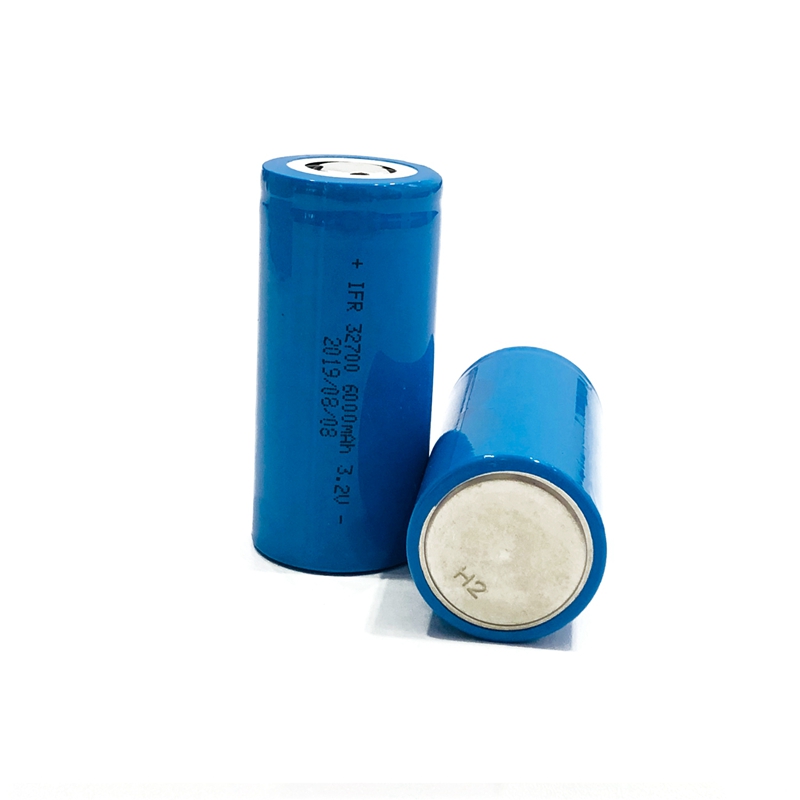
Iron phosphate lithium ion battery
The positive electrode uses lithium iron phosphate. The advantages of iron-phosphate lithium-ion batteries are that they are safe because they cannot be damaged even if the internal heating structure is heated, and the manufacturing cost of iron-based lithium-ion batteries is lower than that of manganese batteries. But the voltage is lower than that of other lithium-ion batteries.
3. Where are lithium-ion batteries used?
The first commercially available lithium-ion batteries for home appliances were used in video cameras in the first half of the 1990s to make them small and lightweight. After that, the mobile phone was used in succession, and the market demand soared. Today, lithium-ion batteries are widely used in every scene of our lives, such as smartphones, laptops, electric cars, electric bicycles and other fields.
Follow us and explore more! 👉 Facebook