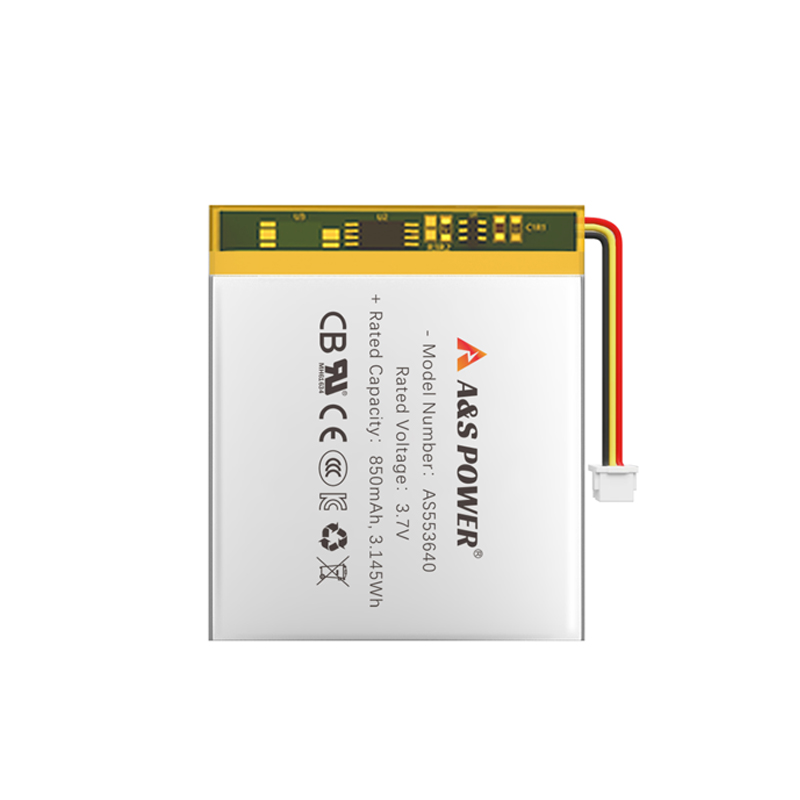
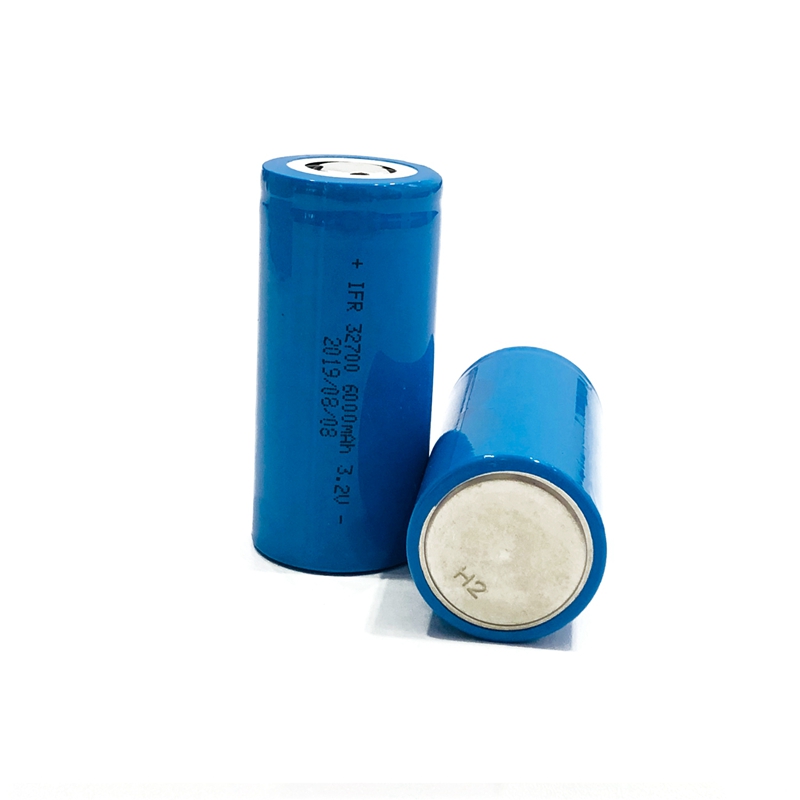
Battery
Application
Hot product
Contact us
Li-ion battery energy storage technology will still be irreplaceable!
2021-07-02
Introduction: A German-Israeli research team has gathered for three days to discuss which energy storage technologies may outperform lithium-ion batteries in the future. Their conclusion is that there is no such thing as a "post-lithium-ion era". They suggest adopting a "side-by-side" approach to multiple technologies in different applications and the mix of technologies. The group emphasized the strong potential of redox flow storage, although it is only suitable for stationary applications, they believe it may outperform lithium-ion batteries.
Researchers from the German Institute and the Technion-Israel Institute of Technology began a three-day discussion on the future of energy storage.
They discussed an energy storage technology that may be considered a reliable alternative to lithium-ion energy storage, and their conclusion is clear: the "post-lithium-ion" era is not yet over.
The researchers said: "After extensive discussions, the research team has concluded that the current atmosphere of future technological demand after the lithium era and the pursuit of new technologies that can replace lithium battery technology are somewhat inappropriate and misleading."
Instead, they recommend a "parallel" approach to all energy storage technologies. They also identified technologies that they believe are more promising for the future.
Sodium-ion batteries (Na-Ion) rely on the same ion energy storage principle of lithium-ion technology and are considered an interesting alternative because they can provide a burden due to potential shortages of lithium and cobalt, or possible price spikes Affordable solution. They are also easy to transport and have great potential to further reduce raw material costs. The group said: "In fact, the cost and environmental friendliness of the layered oxide cathode materials proposed so far seem to be the main advantages of sodium ion batteries."
The report added that sodium-ion batteries face similar safety issues as lithium-ion batteries in large-scale applications, but the development is still limited, and there is not enough understanding of the failure modes, mechanisms and analysis of the entire battery level. It is recommended for use in stationary energy storage systems and light vehicles for short-distance transportation.
The main advantages of redox flow energy storage are the scalability of energy storage capacity, the ability to operate at most ambient temperatures, and long-term energy storage capacity.
The research team explained: “Redox flow batteries are expected to surpass lithium-ion batteries only in static applications, because their key feature is to store energy-containing chemicals in external reservoirs, which can be stored from renewable resources during peak production periods. Energy and energy, and supply when production drops. At the same time, the development of advanced materials and chemistry is considered necessary to overcome the limitations of existing concepts and improve system performance."
According to the analysis of the micro-lithium battery group, in metal-air batteries and energy storage devices based on multivalent metal anodes, lithium-ion battery technology will remain vital for many years to come.

Researchers from the German Institute and the Technion-Israel Institute of Technology began a three-day discussion on the future of energy storage.
They discussed an energy storage technology that may be considered a reliable alternative to lithium-ion energy storage, and their conclusion is clear: the "post-lithium-ion" era is not yet over.
The researchers said: "After extensive discussions, the research team has concluded that the current atmosphere of future technological demand after the lithium era and the pursuit of new technologies that can replace lithium battery technology are somewhat inappropriate and misleading."
Instead, they recommend a "parallel" approach to all energy storage technologies. They also identified technologies that they believe are more promising for the future.
Sodium-ion batteries (Na-Ion) rely on the same ion energy storage principle of lithium-ion technology and are considered an interesting alternative because they can provide a burden due to potential shortages of lithium and cobalt, or possible price spikes Affordable solution. They are also easy to transport and have great potential to further reduce raw material costs. The group said: "In fact, the cost and environmental friendliness of the layered oxide cathode materials proposed so far seem to be the main advantages of sodium ion batteries."
The report added that sodium-ion batteries face similar safety issues as lithium-ion batteries in large-scale applications, but the development is still limited, and there is not enough understanding of the failure modes, mechanisms and analysis of the entire battery level. It is recommended for use in stationary energy storage systems and light vehicles for short-distance transportation.
The main advantages of redox flow energy storage are the scalability of energy storage capacity, the ability to operate at most ambient temperatures, and long-term energy storage capacity.
The research team explained: “Redox flow batteries are expected to surpass lithium-ion batteries only in static applications, because their key feature is to store energy-containing chemicals in external reservoirs, which can be stored from renewable resources during peak production periods. Energy and energy, and supply when production drops. At the same time, the development of advanced materials and chemistry is considered necessary to overcome the limitations of existing concepts and improve system performance."
According to the analysis of the micro-lithium battery group, in metal-air batteries and energy storage devices based on multivalent metal anodes, lithium-ion battery technology will remain vital for many years to come.