What is the Difference Between LiFePO4 and LiIon?
If you want to know the Difference Between LiFePO4 and LiIon batteries, you need to look at safety, stability, and market trends. You will find that a LiFePO4 battery offers greater safety and thermal stability compared to other lithium-ion types, making it a smart choice for users concerned about battery fires or overheating. Recent market data shows strong growth for LiFePO4, especially in electric mobility and renewable energy.
- The LiFePO4 market reached USD 1.23 billion in 2024 and continues to grow.
- Many consumers now seek batteries made with safer, more sustainable materials.
By understanding these differences, you can make a more informed choice and select the battery that best fits your needs.
Key Takeaways
- LiFePO4 batteries offer superior safety and thermal stability, making them ideal for applications where fire risk is a concern.
- With a lifespan of 2,000 to 10,000 cycles, LiFePO4 batteries last significantly longer than traditional lithium-ion batteries, which typically last 500 to 2,000 cycles.
- LiFePO4 batteries are more cost-effective over time due to their lower initial cost and reduced replacement frequency, making them a smart choice for budget-conscious consumers.
- For portable devices like smartphones and laptops, lithium-ion batteries are preferred due to their higher energy density, allowing for lighter and more compact designs.
- When choosing a battery, consider your specific needs for safety, lifespan, and energy storage capacity to make the best decision for your application.
What Is LiFePO4?
Key Features
You will find that a lifepo4 battery, also known as a lithium iron phosphate battery, stands out for its unique chemistry and structure. This battery uses lithium iron phosphate as the cathode material, which gives it a strong foundation for safety and stability. The core components of a lifepo4 battery include a lithium iron phosphate cathode, a graphite anode, and a non-flammable electrolyte. This combination helps you avoid many of the risks found in other lithium-ion batteries.
Here is a quick overview of the main components and characteristics:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Cathode Material | Lifepo4 is used in lithium-ion batteries for energy storage and electric vehicles. |
| Cycle Stability | Over 2000 cycles of charging and discharging, indicating durability. |
| Safety | It is safe, nontoxic, and low in cost, making it a favorable option. |
| Limitations | Low capacity and low bulk density hinder further development. |
A lifepo4 battery delivers a round-trip efficiency of up to 98%. You can expect it to perform well even under tough conditions, with stable operation at temperatures up to 60°C. Most lifepo4 batteries offer energy densities between 90 and 160 Wh/kg, which is lower than some other lithium-ion types, but you gain significant safety and longevity.
Benefits
When you choose a lifepo4 battery, you benefit from a long cycle life. Many models last between 2,000 and 5,000 cycles, and some reach up to 10,000 cycles. This means you can rely on your lithium iron phosphate battery for years, even with frequent use. The chemistry of lifepo4 makes it highly resistant to overheating and thermal runaway, so you reduce the risk of fire or explosion.
Tip: If you need a battery for solar energy storage or electric vehicles, a lifepo4 battery offers a safer and more stable choice than many alternatives.
You also enjoy high efficiency, with minimal energy loss during charging and discharging. The non-toxic materials in a lithium iron phosphate battery make it an environmentally friendly option. While the energy density is not the highest, the trade-off comes in the form of unmatched safety and durability. Lifepo4 batteries also require less maintenance, so you spend less time worrying about performance and more time focusing on your projects.
What Is LiIon?
A lithium ion battery powers many of the devices you use every day. You find this technology in smartphones, laptops, electric vehicles, and even renewable energy systems. The lithium ion battery stands out for its high energy density and versatility, making it a popular choice across industries.
Main Types
You can choose from several main types of lithium ion battery, each with unique strengths. The most common types include:
- Lithium Cobalt Oxide (LCO): This lithium ion battery offers high energy density, which makes it ideal for portable electronics. However, it has a shorter lifespan and lower thermal stability.
- Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NCM): You get a balance of energy density and lifespan with this lithium ion battery. It works well in electric vehicles and power tools.
- Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP): This type provides excellent thermal stability and safety. Many users select it for applications where safety is a top priority.
- Lithium Titanate (LTO): You benefit from a very long lifespan and high thermal stability, though the energy density is lower.
Here is a quick comparison to help you understand the differences:
| Battery Type | Energy Density | Lifespan | Thermal Stability | Safety |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCO | High | Short | Low | Moderate |
| NCM | High | Long | Moderate | Good |
| LFP | Moderate | Long | High | Very Good |
| LTO | Low | Very Long | High | Excellent |
Note: When you select a lithium ion battery, consider your needs for energy density, safety, and lifespan.
Advantages
You gain several important benefits when you use a lithium ion battery:
- Extended operational lifetimes. A lithium ion battery can last between 500 and 2,000 charge-discharge cycles, which means you replace batteries less often.
- Lower total cost of ownership. Even though the initial price may be higher, the efficiency and long lifespan of a lithium ion battery reduce your overall costs.
- Environmental benefits. A lithium ion battery does not contain toxic heavy metals, so you help reduce environmental impact and greenhouse gas emissions.
A lithium ion battery gives you reliable performance, flexibility, and a strong safety profile when you choose the right type for your application. You can trust this technology to deliver power efficiently and safely in many different settings.
Difference Between LiFePO4 and LiIon
When you compare batteries, you need to look at the difference between lifepo4 and lithium ion across several important factors. Each type has unique strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right battery for your needs.
Chemical Composition
The main difference between lifepo4 and lithium ion batteries starts with their chemistry. LiFePO4 batteries use lithium iron phosphate as the cathode material. This structure gives you excellent thermal stability and a lower risk of fire. In contrast, most lithium ion batteries use materials like nickel manganese cobalt (NMC) or nickel cobalt aluminum (NCA) for the cathode. These materials provide higher energy density but can increase the risk of overheating. The chemical makeup of each battery type directly affects its performance, safety, and lifespan.
Energy Density
Energy density measures how much energy a battery can store for its weight. Here is a side-by-side comparison:
| Battery Type | Specific Energy (Wh/kg) |
|---|---|
| LiFePO4 | 90–160 |
| Li-ion (NMC/NCA) | 150–250 (up to 300) |
You will notice that the difference between lifepo4 and lithium ion is clear in this area. LiFePO4 batteries usually have a specific energy of 90–160 Wh/kg. Conventional lithium ion batteries can reach 150–250 Wh/kg, with some advanced types going even higher. This means lithium ion batteries are better for applications where weight and size matter, such as smartphones or laptops. However, LiFePO4 batteries trade some energy density for greater safety and a long service life.
Note: If you need a battery for portable devices, lithium ion may be the better choice due to its higher energy density.
Voltage
Voltage is another key factor in the difference between lifepo4 and lithium ion batteries. LiFePO4 batteries have a nominal voltage of 3.2V per cell. Most lithium ion batteries, such as NMC or NCA, have a nominal voltage of 3.6V or 3.7V per cell. This difference affects how you design battery packs for different applications.
| Voltage Type | LiFePO4 (1 Cell) | Li-ion (NMC/NCA, 1 Cell) |
|---|---|---|
| Nominal | 3.2V | 3.6–3.7V |
| Maximum | 3.65V | 4.2V |
| Minimum | 2.5V | 2.5–3.0V |
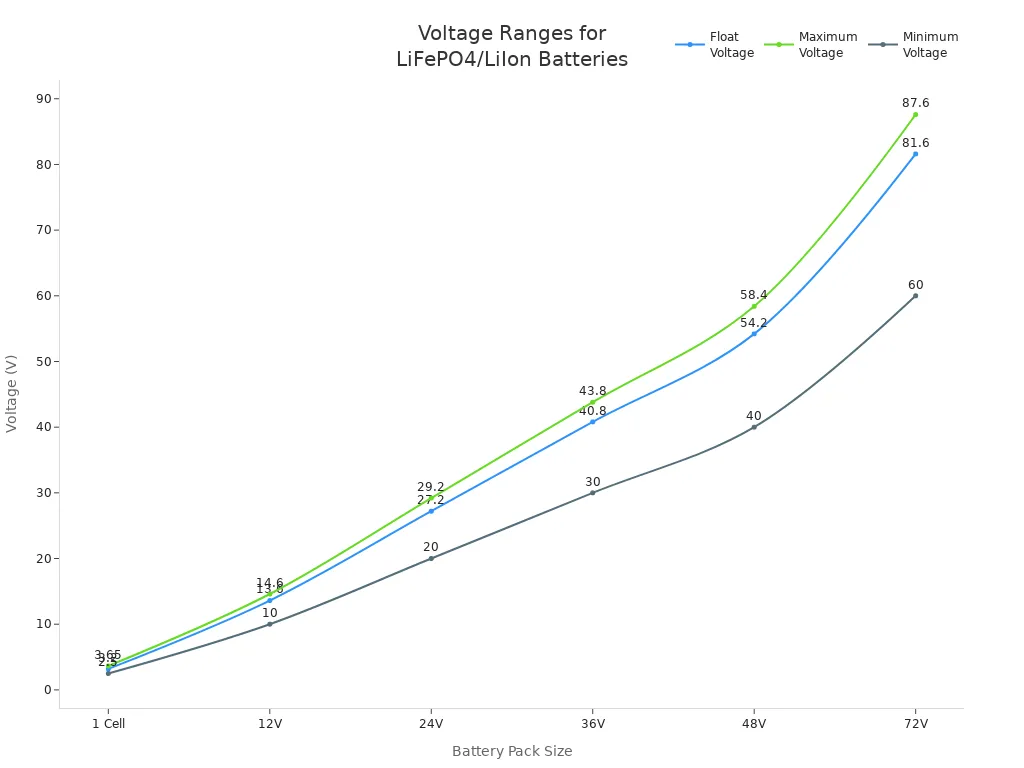
You should consider voltage when replacing or upgrading batteries, as using the wrong type can affect device performance.
Lifespan
The expected life-cycle of lithium iron phosphate technology stands out as one of its biggest advantages. LiFePO4 batteries typically last between 6 to 10 years, depending on how you use and maintain them. Many models offer over 2,000 charge-discharge cycles, with some reaching up to 10,000 cycles. In contrast, most lithium ion batteries last between 500 and 2,000 cycles. This difference between lifepo4 and lithium ion means you will replace lithium ion batteries more often, especially in demanding applications.
- LiFePO4: 6–10 years, 2,000–10,000 cycles
- Lithium ion: 2–5 years, 500–2,000 cycles
If you want a battery with a long service life, LiFePO4 is the clear winner.
Safety
Safety is a top concern for anyone using batteries. The difference between lifepo4 and lithium ion is significant here. LiFePO4 batteries are generally considered safer than lithium ion batteries. Their chemistry resists overheating and thermal runaway, which greatly reduces the risk of fire or explosion. Lithium ion batteries have a very low failure rate—less than one in a million—but incidents can still occur, especially with non-certified brands or poor handling.
- LiFePO4 batteries rarely overheat or catch fire.
- Lithium ion batteries can pose risks if damaged or improperly charged.
- The FAA recorded over 200 incidents involving lithium ion batteries between 1991 and 2018, often linked to misuse.
If safety is your priority, you should choose LiFePO4.
Cost
Cost is another important factor in the difference between lifepo4 and lithium ion batteries. LiFePO4 batteries are about 20–30% cheaper per kWh than NMC lithium ion batteries. The lower raw material costs make LiFePO4 more accessible for many consumers. You will find these batteries in budget-friendly electric vehicles, buses, and solar storage systems. While system integration costs are only slightly lower, the initial price advantage makes LiFePO4 a popular choice for affordability-driven markets.
- Lower upfront cost for LiFePO4 batteries
- More cost-effective over the battery’s lifetime
- Ideal for large-scale or budget-conscious projects
Tip: If you want to maximize value and minimize replacement costs, LiFePO4 batteries offer a strong advantage.
LiFePO4 vs Lithium Ion: Applications

Best Uses for LiFePO4
You will find that lifepo4 vs lithium ion comparisons often highlight the unique strengths of LiFePO4 in specific applications. When you need a battery that delivers long life, safety, and reliable storage, LiFePO4 stands out. Many electric vehicles now use this battery because it offers stable performance and reduces fire risk. You also see lifepo4 vs lithium ion debates in the solar power industry, where LiFePO4 provides dependable energy storage for homes and businesses. This battery helps you store solar energy during the day and use it at night or during cloudy weather.
You can also use LiFePO4 batteries in RVs and yachts. These vehicles require lightweight and compact storage solutions, and LiFePO4 meets these needs. The battery’s long lifespan means you replace it less often, saving you time and money. Here are some of the most common uses:
- Electric vehicles: You get safe, long-lasting power for cars and buses.
- Solar power systems: You can store solar energy efficiently for later use.
- RVs: You power appliances and electronics with reliable storage.
- Yachts: You benefit from lightweight, durable battery storage on the water.
Tip: If you want a battery for off-grid storage or mobile applications, lifepo4 vs lithium ion comparisons show LiFePO4 as the safer and more cost-effective choice.
Best Uses for LiIon
When you compare lifepo4 vs lithium ion, you see that lithium ion batteries excel in devices where high energy density and compact size matter most. You use this battery in smartphones, laptops, and tablets because it stores more energy in a smaller space. This makes your devices lighter and lets you use them longer between charges. Lifepo4 vs lithium ion discussions also show that lithium ion batteries power many electric vehicles, especially those that need longer driving ranges.
You find lithium ion batteries in e-bikes, where efficient storage supports long rides. The battery’s flexibility and high energy density make it ideal for portable electronics and transportation. Here are the most common uses:
- Smartphones: You enjoy longer battery life and slim designs.
- Laptop computers: You benefit from extended use and lightweight storage.
- Electric vehicles: You get high-performance storage for cars like Tesla and Nissan Leaf.
- E-bikes: You experience greater pedal-assist range with efficient battery storage.
| Trend/Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Increasing Demand | Environmental concerns and regulations drive lifepo4 vs lithium ion adoption in transportation. |
| Technological Advancements | Better battery storage, range, and safety boost consumer confidence. |
| Cost Reduction | Lower prices make lifepo4 vs lithium ion batteries more accessible for EVs and storage systems. |
| Geographic Expansion | Local battery industries grow to support energy independence and reduce costs. |
| Sustainable Recycling Techniques | Improved recycling reduces the environmental impact of battery storage. |
| Battery Management Systems (BMS) | Enhanced BMS increases battery life, performance, and safety in lifepo4 vs lithium ion systems. |
Note: Lifepo4 vs lithium ion trends show both battery types growing in popularity, but your choice depends on your storage needs and application.
Choosing the Right Battery
Factors to Consider
Selecting the right battery for your energy storage needs requires careful evaluation of several important factors. You should focus on the following points to ensure your choice matches your requirements for safety, performance, and cost-effectiveness:
-
Energy Storage Capacity
Assess your household’s energy storage needs and budget. The battery must provide enough capacity to support your daily usage, especially for stationary energy storage systems. -
Charge-Discharge Efficiency
Look for a battery with high efficiency to minimize energy loss during charging and discharging. Efficient batteries help you maximize the value of your energy storage investment. -
Cycle Life
Choose a battery with a long cycle life. This reduces maintenance costs and ensures reliable energy storage over many years. -
Safety Performance
Prioritize batteries with high safety features. A very safe and secure technology protects your home and family from accidents. -
Brand Reputation and After-Sales Service
Select reputable brands that offer strong support and warranties. Reliable service ensures you get help when you need it. -
Cost
Consider the price of the battery in relation to its capacity and potential savings. A higher initial cost may be justified by longer lifespan and lower replacement frequency.
For portable electronics, you need to evaluate different criteria. The following table summarizes the most important aspects:
| Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
| Shelf Life | The duration a battery can be stored unused before performance drops. |
| Rechargeable / Non-Rechargeable | Whether the battery can be reused or is single-use. |
| Size | The physical dimensions must fit the device’s design. |
| Operating Temperature | The temperature range in which the battery performs well. |
| Capacity | The amount of energy storage available for device runtime. |
| Battery Chemistry | The type of chemistry affects performance and suitability. |
| Cost | The financial impact on the overall device cost. |
Tip: Always match the battery’s specifications to your application, whether you need energy storage for your home or portable electronics.
Lithium Iron Phosphate Technology
How It Works
You interact with lithium iron phosphate technology every time you use an LFP battery. This technology uses iron phosphate as the cathode material, which sets it apart from other lithium-based batteries that often use cobalt or manganese oxides. The unique chemical structure of LFP batteries gives you several important benefits. The strong covalent bonds between oxygen and phosphorus atoms in the cathode create exceptional thermal stability. This means your LFP battery can handle high temperatures and mechanical stress without breaking down or catching fire.
LFP batteries also stand out for their ability to deliver consistent power in a wide range of conditions. You can rely on them in both hot and cold environments. The chemistry of lithium iron phosphate technology allows for thousands of charge and discharge cycles. You get a battery that lasts much longer than traditional lithium-ion options. The absence of toxic heavy metals in LFP batteries makes them safer for you and better for the environment.
Note: LFP batteries can withstand short circuits and physical impacts, making them ideal for demanding applications like electric vehicles and industrial equipment.
Why It Matters
You benefit from lithium iron phosphate technology in many ways. The enhanced safety of LFP batteries comes from their stable chemistry. You reduce the risk of thermal runaway, which is a major cause of battery fires. This makes LFP batteries a top choice for electric vehicles, solar energy storage, and backup power systems where safety is critical.
LFP batteries also give you a longer lifespan. You can expect up to 3,000 charge cycles or more, which means fewer replacements and lower costs over time. This durability helps you save money and reduces waste, supporting a cleaner environment. LFP batteries perform well in extreme temperatures, so you can use them in harsh climates without worrying about performance drops.
Here are the unique advantages you gain from lithium iron phosphate technology:
- Enhanced safety and thermal stability
- Long-lasting performance with thousands of cycles
- Eco-friendly materials that protect the environment
- Reliable operation in extreme temperatures
- Lower total cost of ownership
You make a smart investment when you choose LFP batteries. Their combination of safety, longevity, and environmental benefits makes them the preferred solution for many modern energy needs.
You now see the key differences between LiFePO4 and LiIon batteries. The table below highlights the most important features:
| Feature | LiFePO4 | LiIon |
|---|---|---|
| Lifespan | 2500+ cycles | 500–1000 cycles |
| Energy Density | Moderate | Higher |
| Safety | Enhanced | Less stable |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Best Use | Solar, long-term use | Portable devices, EVs |
Choose a LiFePO4 battery for safety, long life, and solar storage. Pick a LiIon battery when you need high energy in a small space. If you have questions about battery charging or want to discuss cooperation, reach out to our team.
-
 May.2026.02.27Lithium-Ion Batteries: The Six Constraints Blocking the Path to PerfectionLearn More
May.2026.02.27Lithium-Ion Batteries: The Six Constraints Blocking the Path to PerfectionLearn More -

 May.2026.02.25Li-Polymer Battery 5000mAh: Complete Technical & OEM GuideLearn More
May.2026.02.25Li-Polymer Battery 5000mAh: Complete Technical & OEM GuideLearn More -
 May.2026.02.24The Unparalleled Advantages of Lithium-Ion Batteries Over Traditional BatteriesLearn More
May.2026.02.24The Unparalleled Advantages of Lithium-Ion Batteries Over Traditional BatteriesLearn More -
 May.2026.02.243.6 Volt Battery: Complete Technical Guide for Engineers & BuyersLearn More
May.2026.02.243.6 Volt Battery: Complete Technical Guide for Engineers & BuyersLearn More -
 May.2026.02.24What Is a 3.8V LiPo Battery? A Complete Engineering & OEM GuideLearn More
May.2026.02.24What Is a 3.8V LiPo Battery? A Complete Engineering & OEM GuideLearn More