Why Lithium-ion Batteries are Popular?
You choose lithium-ion batteries because they deliver high energy density, allowing you to power devices for longer periods. These batteries offer a long lifespan, so you replace your battery less often. Their lightweight design makes portable electronics easier to carry. Fast charging keeps your devices ready with minimal downtime. You benefit from low maintenance and fewer environmental concerns compared to older battery technologies.
Key Takeaways
- Lithium-ion batteries provide high energy density, allowing devices to run longer without frequent recharging.
- These batteries have a long lifespan, reducing the need for replacements and saving you money over time.
- Their lightweight design makes them ideal for portable electronics, enhancing convenience and usability.
- Fast charging capabilities minimize downtime, ensuring your devices are ready when you need them.
- Choosing lithium-ion batteries supports environmental sustainability through lower waste and recyclability.
Advantages

High Energy Density
You rely on lithium-ion batteries because they deliver more energy in a smaller and lighter package than other rechargeable options. This high energy density allows you to use compact devices that run longer between charges. The following table compares the energy density of lithium-ion batteries with other common types:
| Battery Type | Energy Density (Wh/kg) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Lithium-ion | 200-300 | Current energy density |
| Lithium-ion (future) | 500-750 | Projected energy densities for 2030s-2040s |
| Lead acid | 30-50 | Traditional automotive and backup use |
| Nickel-cadmium | 45-80 | Older rechargeable technology |
| Sodium-ion | < 200 | Emerging alternative |
Lithium-ion batteries typically offer an energy density ranging from 50 to 260 Wh/kg, which is much higher than nickel-cadmium batteries (45-80 Wh/kg) and lead-acid batteries (30-50 Wh/kg). You benefit from this advantage in electric vehicles, smartphones, and laptops, where weight and efficiency matter most.
Long Lifespan
You expect your battery to last through hundreds or even thousands of charge cycles. Lithium-ion batteries deliver on this promise. The cycle life of these batteries varies by chemistry, but you can see the comparison below:
| Battery Chemistry | Typical Cycle Life Range |
|---|---|
| Lithium-Ion (NMC/NCA) | 500 to 1,500 |
| Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) | 2,000 to 5,000 |
| Lithium Polymer (LiPo) | 300 to 500 |
| Lithium-Titanate (LTO) | 10,000 to 20,000 |
| Solid-State Lithium | 5,000 to 10,000 (potential) |
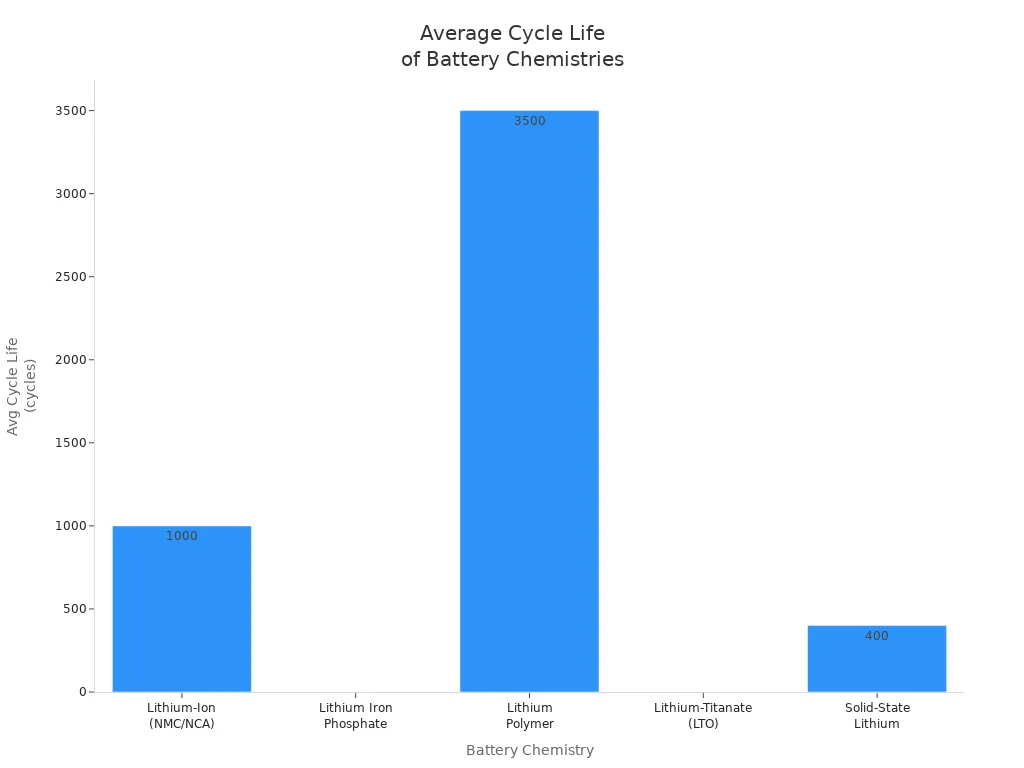
Recent studies show that lithium-ion batteries last longer because they have lower self-discharge rates. Manufacturers reduce the diffusion of protons, which helps extend the lifespan. You replace your battery less often, saving money and reducing waste.
Lightweight
You want your devices to be portable and easy to carry. Lithium-ion batteries help achieve this goal. Their design uses a lithium cathode and a graphite anode, which keeps the battery light. The table below highlights the features that make lithium-ion batteries lighter than other types:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Material Composition | Lithium cathode and graphite anode |
| Energy Density | High energy density means less weight for the same power |
| Weight Comparison | 40-50% lighter than lead-acid batteries |
| Construction | Compact design ideal for mobile applications |
You experience the benefits every time you pick up your phone, laptop, or electric vehicle. The lightweight nature of lithium batteries makes them the preferred choice for portable electronics and transportation.
Fast Charging
You need your devices ready as quickly as possible. Lithium-ion batteries support fast charging, which keeps your downtime to a minimum. Compared to lead-acid batteries, which can take up to 8 hours to charge, lithium-ion batteries usually recharge in 1-2 hours.
| Battery Type | Charging Time |
|---|---|
| Lead Acid | 8 hours |
| Lithium-Ion | 1-2 hours |
Several technological advancements enable this rapid charging:
- Innovations in electrode architecture, such as carbon nanotube networks, boost conductivity.
- Advanced electrolyte formulations with fluorinated solvents improve stability and reduce decomposition.
- Composite anode materials, including graphene and silicon oxide, allow for faster lithium transport.
- Stable solid-electrolyte interphase (SEI) created by atomic layer deposition enhances performance under high-current conditions.
You benefit from these improvements every time you need a quick recharge for your devices.
Low Maintenance
You prefer batteries that require little attention. Lithium-ion batteries are maintenance-free, unlike lead-acid batteries that need regular water refilling and cleaning.
| Battery Type | Maintenance Requirement |
|---|---|
| Lithium-ion | Maintenance-free |
| Lead-acid | Requires regular maintenance |
You save time and money because you do not need to perform routine checks or repairs. Proactive maintenance and troubleshooting support help you resolve minor issues independently. Effective communication from manufacturers keeps you informed about battery performance, which further extends the lifespan.
Tip: Choosing lithium-ion batteries reduces your maintenance costs and minimizes unexpected downtime.
Environmental Benefits
You care about the environment. Lithium-ion batteries offer several advantages over traditional battery technologies:
- Higher energy density means you use fewer batteries, which reduces waste.
- Longer-lasting batteries lower the frequency of replacements, decreasing your carbon footprint.
- Many lithium-ion batteries are recyclable. Materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel can be repurposed, minimizing electronic waste.
- The production process emits fewer greenhouse gases compared to other battery types.
You contribute to a cleaner planet by choosing lithium-ion batteries for your devices and vehicles.
Applications

Consumer Electronics
You use lithium-ion batteries every day in your favorite devices. These batteries power most of your mobile phones, laptops, tablets, and wearable devices. The consumer electronics sector accounts for over 46% of the lithium-ion battery market. You also find these batteries in digital cameras, LED lighting, vacuum cleaners, hearing aids, calculators, and flashlights.
- Mobile phones
- Laptops
- Tablets
- Digital cameras
- Wearable devices
- LED lighting
- Vacuum cleaners
- Hearing aids
- Calculators
- Flashlights
Lithium-ion batteries improve the performance and portability of your devices. The table below shows how advanced battery types enhance your experience:
| Feature | Conventional Lithium-Ion | LTO Lithium-Ion |
|---|---|---|
| Battery Life | Standard | 20% longer |
| Self-Discharge | Higher | Lower |
| Energy Density | Moderate | Enhanced |
| Cycling Stability | Average | Improved |
| Durability | Limited | High |
You benefit from longer battery life, lower self-discharge, and greater durability. These features make your electronics more reliable and convenient.
Electric Vehicles
You see lithium-ion batteries driving the electric vehicle revolution. These batteries offer exceptional energy density, which means you can travel farther on a single charge. Their compact and lightweight design allows manufacturers to build vehicles with longer driving ranges and better efficiency.
- High energy density enables longer trips without frequent charging.
- Lightweight batteries improve vehicle performance and handling.
- Reliable cycling stability supports daily use and fast charging.
You trust lithium-ion batteries to deliver consistent power and safety in your electric car.
Energy Storage
You rely on lithium-ion batteries for advanced energy storage solutions. These batteries play a key role in renewable energy systems, storing solar and wind power for later use. The global market for lithium-ion energy storage reached $17.47 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to nearly $26.71 billion by 2032. Annual deployments now exceed 300 GWh.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Market size in 2024 | USD 17.47 Billion |
| Projected market size by 2032 | Nearly USD 26.71 Billion |
| Projected annual global deployments (GWh) | Exceeding 300 GWh |
Lithium-ion batteries help stabilize the grid and support renewable integration. The chart below highlights their benefits for grid stability:
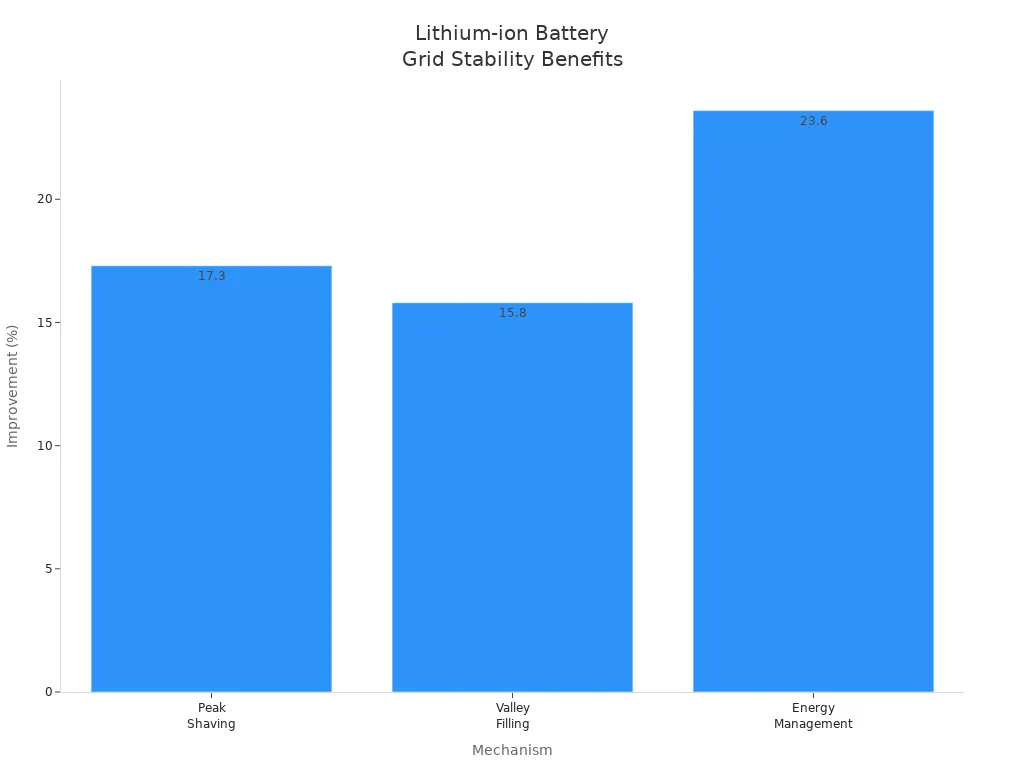
You benefit from peak shaving, valley filling, and improved energy management. These batteries ensure reliable power, even during outages or high demand.
Industrial & Medical
You depend on lithium-ion batteries for critical industrial and medical applications. In factories, these batteries power robots, backup systems, and portable tools. In hospitals, they support life-saving equipment and portable monitors.
| Safety Mechanism | Function |
|---|---|
| PTC Device | Inhibits high current surges |
| Circuit Interrupt Device | Opens path if internal pressure exceeds 10 Bar |
| Safety Vent | Releases gas during rapid pressure increase |
| Electronic Protection | Opens switch if voltage exceeds 4.30V |
| Fuse | Cuts current if temperature nears 90°C |
| Control Circuit | Prevents over-discharging below 2.50V/cell |
You trust these batteries for their reliability and safety features. In medical devices, lithium-ion batteries provide high energy density and long life spans. They deliver consistent voltage, which is vital for chronic disease management and emergency care. Fast charging and long cycle life ensure your devices are always ready when you need them.
Note: Lithium-ion batteries offer unmatched versatility and structural reliability across industries, making them the preferred choice for modern technology.
Drawbacks
Cost
You may notice that lithium-ion batteries often come with a higher upfront cost compared to other battery types. The price per kilowatt-hour can vary based on application and chemistry. For example, automotive packs usually cost between $120 and $180 per kWh, while solar energy storage systems can range from $400 to $800 per kWh. The table below compares the cost per kWh for different battery types:
| Battery Type | Cost per kWh |
|---|---|
| Lead-Acid | $1.20 |
| NiMH | $0.75 |
| LFP Lithium-Ion | $0.20 |
Several factors influence the final price you pay for lithium-ion batteries:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Raw Material Costs | Account for up to 60% of the price; lithium prices can fluctuate sharply. |
| Manufacturing Scale | Large factories lower costs through automation and bulk purchasing. |
| Battery Chemistry | LFP is cheaper but has lower energy density than NMC or NCA. |
| R&D and Policy | Research, development, and government incentives affect pricing. |
| Supply Chain Disruptions | Events like pandemics or trade disputes can cause price spikes. |
You might find that the initial investment is higher, but the longer lifespan and lower maintenance can offset these costs over time.
Safety
You should be aware that lithium-ion batteries carry certain safety risks. Overheating, sparking, and even fires can occur if the battery is damaged or improperly handled. The chart below shows the percentage of businesses affected by different safety incidents:
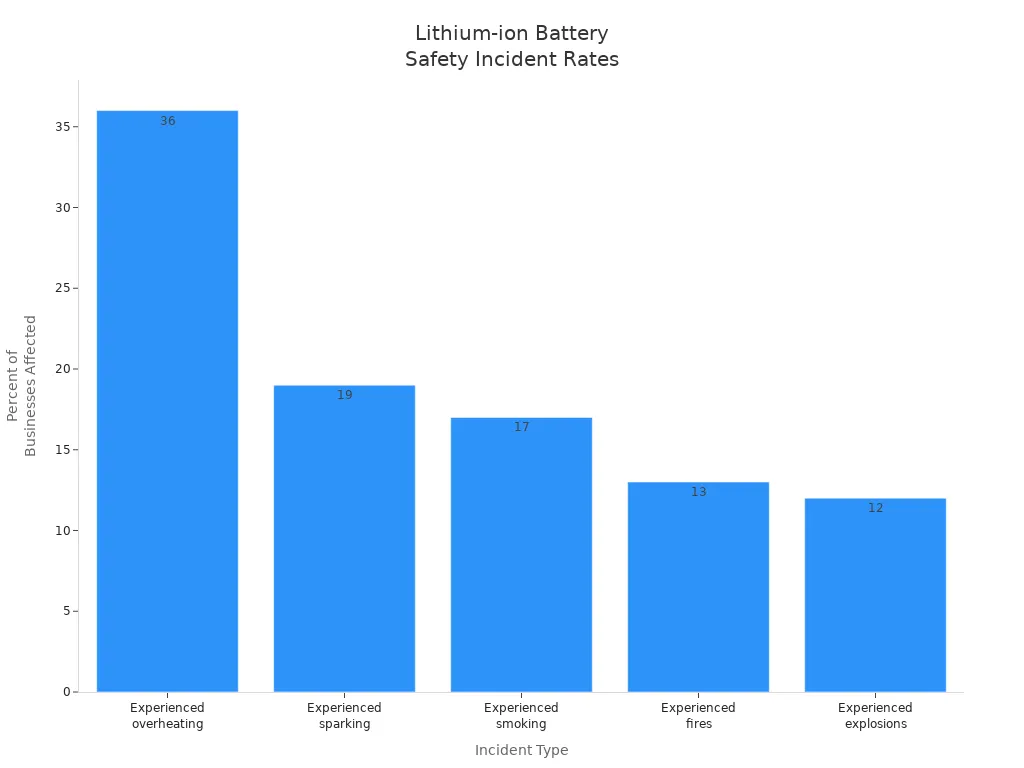
- Over 54% of businesses have experienced incidents related to lithium-ion batteries.
- Nearly 24% of all electric vehicle fires are caused by these batteries.
- In New York City, lithium-ion battery fires led to at least 12 deaths and over 260 injuries between 2021 and 2023.
You can reduce risks by following best practices for storage and handling. Modern safety features, such as smart sensors and digital checklists, help monitor battery health. Proper storage—at room temperature, away from sunlight, and in ventilated areas—also lowers the chance of accidents.
Note: Regular staff training and updated safety protocols are essential for minimizing risks.
Environmental Impact
You should consider the environmental footprint of lithium-ion batteries. The production process uses significant energy and raw materials, which can lead to water contamination and greenhouse gas emissions. The table below outlines the main environmental impacts:
| Aspect | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|
| Raw Material Extraction | Water pollution and ecosystem damage |
| Manufacturing | High energy use and air emissions |
| Usage | CO2 emissions depend on electricity source |
| Disposal & Recycling | Recycling reduces emissions but still generates some pollutants |
The average lifespan of a lithium-ion battery is 5 to 8 years, which means more waste as usage grows. In 2022, China retired 530,000 tons of power batteries, with projections exceeding 2.6 million tons annually by 2028. While recycling can cut greenhouse gas emissions by up to 48%, the global recycling rate remains around 59%. Challenges include limited logistics, regulatory barriers, and uneven access to recycling technology.
Tip: Choosing recycled batteries and supporting better recycling programs can help reduce environmental harm.
You see how the advantages of lithium-ion batteries—high energy density, long lifespan, and versatility—make them the top choice for most rechargeable applications. These batteries power your devices efficiently and require little maintenance. Although you face some drawbacks, new trends promise improvements. Solid-state battery technology, better recycling, smart grid integration, and scalable manufacturing will address current limits. If you have questions about rechargeable battery charging or want to discuss cooperation, reach out to our team.
-
 May.2026.02.27Lithium-Ion Batteries: The Six Constraints Blocking the Path to PerfectionLearn More
May.2026.02.27Lithium-Ion Batteries: The Six Constraints Blocking the Path to PerfectionLearn More -

 May.2026.02.25Li-Polymer Battery 5000mAh: Complete Technical & OEM GuideLearn More
May.2026.02.25Li-Polymer Battery 5000mAh: Complete Technical & OEM GuideLearn More -
 May.2026.02.24The Unparalleled Advantages of Lithium-Ion Batteries Over Traditional BatteriesLearn More
May.2026.02.24The Unparalleled Advantages of Lithium-Ion Batteries Over Traditional BatteriesLearn More -
 May.2026.02.243.6 Volt Battery: Complete Technical Guide for Engineers & BuyersLearn More
May.2026.02.243.6 Volt Battery: Complete Technical Guide for Engineers & BuyersLearn More -
 May.2026.02.24What Is a 3.8V LiPo Battery? A Complete Engineering & OEM GuideLearn More
May.2026.02.24What Is a 3.8V LiPo Battery? A Complete Engineering & OEM GuideLearn More
















