New generation of lithium-ion batteries could hold more charge—without catching fire
Imagine using your phone or driving your electric car. You know the battery will last longer and work safely. New lithium-ion batteries can hold more energy now. They store over 250 Wh/kg, while old ones held only 150 Wh/kg. Advanced thermal management helps keep batteries safe. Better battery management systems also make them safer. This big change in lithium battery technology is important for you. Longer-lasting and safer batteries power your favorite devices and vehicles.
| Feature | Old Generation | New Generation |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density (Wh/kg) | Up to 150 | Over 250 |
| Charge Cycles | 300-500 | More than 1,000 |
| Safety Improvements | Basic safety measures | Advanced systems |
Key Takeaways
- New lithium-ion batteries can store over 250 Wh/kg. This is much better than older batteries. Your devices can work longer before you need to charge them again.
- The new batteries have special safety features. They use materials that do not catch fire. They also have better systems to control heat. These changes help stop overheating and fires. This makes your devices safer to use.
- Solid-state batteries are becoming more popular. They use solid electrolytes. This stops fires and helps them work better. These batteries can give your devices power for a longer time.
- Sodium-ion and LFP batteries cost less and are better for the environment. They are safer and easier to make. This makes them a good choice for future electric cars and devices.
- New battery technology means devices last longer and charge faster. They are also safer. You can trust your electronics and vehicles to work better and longer.
Lithium-ion batteries: More charge, less risk

Energy density improvements
People want their devices to last longer. They also want to charge them less often. New lithium battery technology helps with this. It increases energy density. Energy density is how much energy a battery holds for its weight. If energy density is higher, your phone or car runs longer.
- Next-generation lithium-ion batteries aim for over 300 Wh/kg. This is much more than the 150 to 250 Wh/kg of older batteries.
- Scientists made lithium-air batteries that reach 1,200 Wh/kg. That is four times more than regular lithium-ion batteries.
- Many industries use these new batteries. They have higher gravimetric and volumetric energy densities.
You get benefits from these changes every day. Electric vehicles can go farther now. Portable devices stay charged longer. Companies can make lighter products. Battery performance does not get worse. These changes save you time. You do not need to charge as often. You get more freedom from charging cables.
Safety enhancements
Some people worry about battery fires or overheating. This is a big concern in electric vehicles and strong devices. New lithium battery technology helps with these problems. It uses better materials and smarter systems to keep you safe.
| Mechanism | Description |
|---|---|
| Intrinsically safe materials | Materials that lower fire risk by fixing hazards at the source. |
| Thermal runaway mitigation | Software and hardware that reduce the danger of thermal runaway. |
| Nonflammable electrolytes | Electrolytes that do not catch fire, making batteries safer. |
| Solid-state electrolytes | Electrolytes that do not burn and stop dendrite growth, which can cause shorts. |
| High-temperature resistant separators | Separators that do not melt at high heat, lowering fire risk. |
| Battery management systems | Systems that watch battery conditions and handle overheating or danger by themselves. |
Researchers test these safety features in labs and real life. They use many advanced methods to make sure batteries are safe:
| Testing Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) | Small AC signals check inside resistance and damage. This helps find problems early and watch batteries in real time. |
| Thermal Runaway Testing | Finds too much heat and gas early. This stops big failures in things like electric vehicles. |
| X-ray Computed Tomography (CT) | This imaging shows the inside of batteries. It lets people see battery parts without opening them. |
| Gas Analysis Technology | This measures gases during use. It helps find out why batteries break down, like when electrolytes break or batteries get too much charge. |
You can trust new lithium-ion batteries to give more charge with less risk. These changes are good for you and for companies. Safer batteries mean fewer recalls and less downtime. Products work better and last longer. Electric vehicles are safer to drive. Portable electronics are more reliable. You can feel safe knowing lithium battery technology keeps getting better. This makes your life easier and safer.
Battery technology: Current challenges
Overheating and fire risks
Batteries in your devices or cars can be risky. The biggest worry is overheating and fire. Many things can cause these problems:
- Charging too much or letting the battery get too empty
- Very hot or cold weather around you
- Not enough airflow or poor cooling
- Dropping or hitting the battery
Thermal runaway is the worst thing that can happen. The battery gets hotter and hotter without stopping. The solid electrolyte interphase layer breaks apart. The anode, cathode, and electrolyte react together. This starts a chain reaction. It can make smoke, fire, or even explosions.
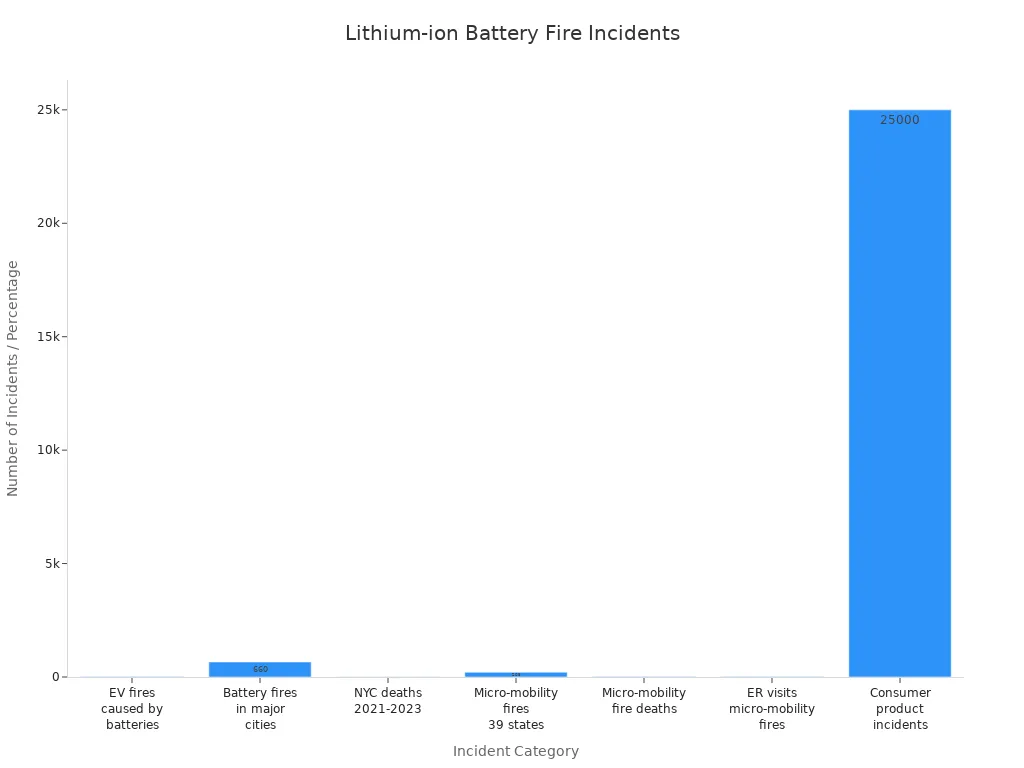
You might ask how often this happens. The numbers show battery fires do happen. Here is a table with some recent facts:
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Percentage of EV fires caused by lithium-ion batteries | 24% |
| Total lithium-ion battery fires reported in major cities (6 years) | 660 |
| Deaths in New York City from 2021 to 2023 | 12 |
| Nationwide micro-mobility device fires in 39 states (2 years) | 208 |
| Total deaths from micro-mobility device fires | 19 |
| Emergency room visits due to injuries from micro-mobility device fires | 22 |
| Overheating or fire incidents in consumer products (5 years) | 25,000 |
Electric vehicles are less likely to catch fire than gas cars. In the UK, only 0.24% of car fires were electric cars. In Sweden, it was just 0.004%.
Limitations of traditional materials
Old lithium-ion batteries use materials that have limits. These limits affect safety and how well batteries work. You may see your device lose charge faster as it gets older. This happens because of some material problems:
- Not using all the material inside the battery
- Damage from stress on the battery
- Losing battery power over time
- Risk of thermal runaway
- Slow lithium-ion movement between electrodes
- Not enough lithium ions when charging fast
- Big material pieces make lithium move slowly
These issues slow down battery progress. They also make it hard for batteries to be safer and last longer.
Note: New research is working to fix these problems with better materials and smarter designs. You will see safer and better batteries as these new ideas are used.
Advances in lithium battery technology

Solid-state electrolytes
Solid-state batteries are safer and hold more energy. They use solid electrolytes, not liquids. This makes them less likely to catch fire. They also stay cooler and work better. You can use your devices longer before charging. Here are some main benefits:
- Solid-state batteries have more energy and are safer than old ones.
- Solid electrolytes help ions move and make batteries last longer.
- These batteries do not burn easily and stay cool.
- New materials help lithium ions move faster, so batteries work better.
But making lots of solid-state batteries is hard. Materials like lithium metal and silicon can change size and grow dendrites. This can cause problems inside the battery. Solid parts touching each other can make it harder for power to flow. This can make batteries fail more often. These batteries can also cost more and weigh more. Electric cars may need more cooling and pressure to use them.
Silicon and new anode materials
New batteries use silicon and other new anode materials. Silicon anodes can hold more energy than graphite. This means batteries last longer and work better. The table below shows how these new materials help batteries:
| Performance Improvement | Description |
|---|---|
| Higher Theoretical Capacity | Silicon holds more energy and costs less than graphite. |
| Volume Expansion Management | Nano-silicon controls swelling but uses more lithium ions. |
| Stable SEI Formation | SiOx helps make stable layers and improves battery life. |
| Enhanced Conductivity | Mixing silicon with carbon helps electricity move faster. |
| Improved Cycle Stability | Doped silicon anodes last longer but lose some power at first. |
But silicon anodes can get much bigger when charging. They can swell over 300%. This swelling can break the battery and make it lose power. The SEI layer can also break down. This makes the battery lose more lithium and not last as long.
Fast charging and longer lifespan
You want batteries that charge fast and last long. New lithium batteries can do both. Fast-charging batteries reach 80% in less than ten minutes. Old batteries needed up to an hour. New batteries keep over 90% power after 1,000 fast charges. Old ones drop to 60-70%. Graphene and silicon oxide help lithium ions move faster. This gives you better batteries.
Tests show electric car batteries last up to 38% longer than lab tests say. Driving in real life helps batteries age slower than charging all the time. This means your cars and devices work well for more years. New battery technology keeps getting better. You get safer, faster, and longer-lasting power.
Alternatives and future outlook
Sodium-ion and LFP batteries
You might hear about new batteries like sodium-ion and LFP. These batteries are safer and cost less for your devices and cars. Sodium-ion batteries use sodium, which is easy to find. This makes them cheaper and simple to make. LFP batteries use iron and phosphate. These are also common and safe to use.
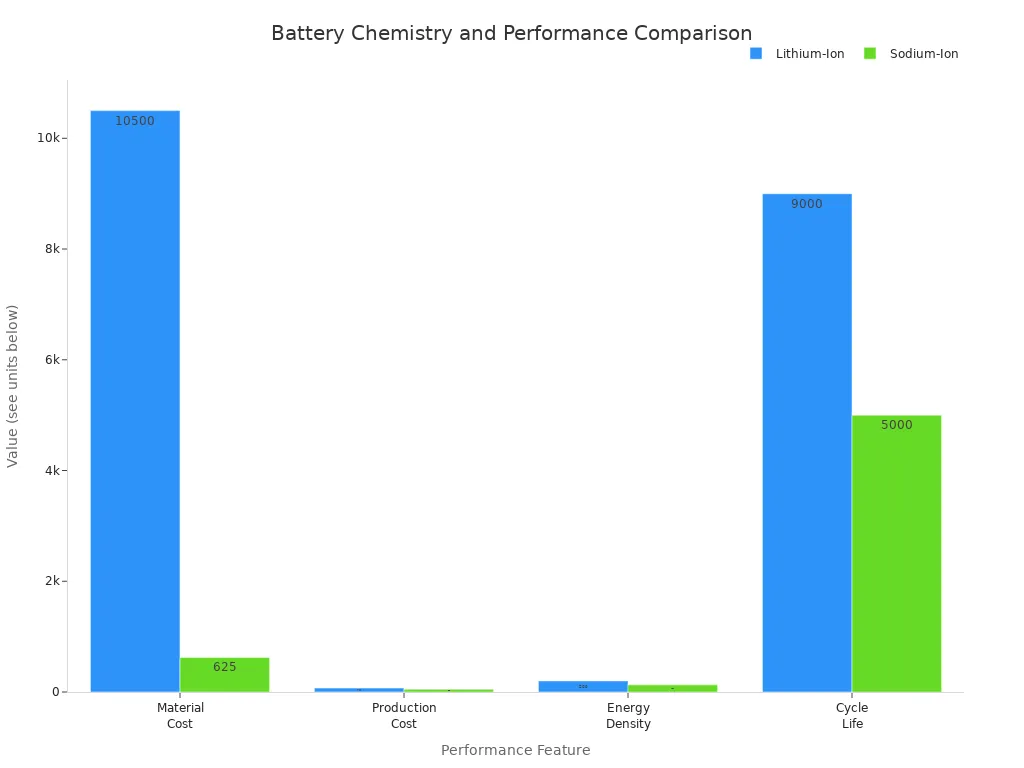
Here is a quick table that compares lithium-ion and sodium-ion batteries:
| Feature | Lithium-Ion Batteries | Sodium-Ion Batteries |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | Rare | Abundant |
| Environmental Impact | Higher | Lower |
| Material Costs | $10,000 - $11,000/ton | $600 - $650/ton |
| Production Costs | $70/kWh | $50/kWh |
| Energy Density | 100-300 Wh/kg | 100-160 Wh/kg |
| Charging | Slower | Faster |
| Cycle Life | 8,000-10,000 | 5,000 |
| Safety | Flammable | More stable |
| Weight | Lighter | Heavier |
| Shipping | Hazardous | Standard |
Sodium-ion batteries are very safe in tests. They do not catch fire and still work if broken. LFP batteries are also known for being safe. Both types are good for electric cars, especially in cities.
Cost and commercial adoption
You want batteries that are cheap and last long. Sodium-ion batteries cost about $125 per kWh now. Experts think the price will drop to $30 per kWh by 2045. LFP batteries cost between $50 and $70 per kWh. As more companies use these batteries, prices will go down.
Many groups are working on these new batteries. For example:
- AM Batteries, Inc. got $2.8 million to make dry electrode sodium-ion batteries.
- Argonne National Laboratory is making hard carbon for sodium-ion batteries.
- Clean Republic is making green sodium-ion cathodes.
Big projects, like the Flatiron 200 MW battery system in Massachusetts, show companies believe in these batteries. Farasis Energy wants to start making semi-solid-state batteries in 2026. You will see more cars and devices using these safer, cheaper batteries soon.
Note: Solid-state and semi-solid-state batteries are coming too. Experts think battery technology will change a lot in the next ten years.
You get better batteries that give more power and are safer. Companies use new materials and smart systems to make batteries cheaper. They also recycle batteries to help the environment. Experts think most cars and devices will have these batteries by 2030.
| Key Impact | Description |
|---|---|
| Higher Capacity | Devices work longer and charge up faster |
| Improved Safety | Fewer fires happen and daily use is safer |
| Sustainability | Recycling lowers pollution and saves resources |
You will notice cleaner energy, smarter tech, and safer things every day.
-
 May.2026.02.27Lithium-Ion Batteries: The Six Constraints Blocking the Path to PerfectionLearn More
May.2026.02.27Lithium-Ion Batteries: The Six Constraints Blocking the Path to PerfectionLearn More -

 May.2026.02.25Li-Polymer Battery 5000mAh: Complete Technical & OEM GuideLearn More
May.2026.02.25Li-Polymer Battery 5000mAh: Complete Technical & OEM GuideLearn More -
 May.2026.02.24The Unparalleled Advantages of Lithium-Ion Batteries Over Traditional BatteriesLearn More
May.2026.02.24The Unparalleled Advantages of Lithium-Ion Batteries Over Traditional BatteriesLearn More -
 May.2026.02.243.6 Volt Battery: Complete Technical Guide for Engineers & BuyersLearn More
May.2026.02.243.6 Volt Battery: Complete Technical Guide for Engineers & BuyersLearn More -
 May.2026.02.24What Is a 3.8V LiPo Battery? A Complete Engineering & OEM GuideLearn More
May.2026.02.24What Is a 3.8V LiPo Battery? A Complete Engineering & OEM GuideLearn More
















