12V STD vs AGM vs Lithium Batteries Key Differences and Which to Choose
When you compare 12V STD, AGM and Lithium batteries, you see clear differences in cost, maintenance, lifespan and compatibility. If you want the lowest upfront cost, choose a standard lead-acid battery, typically priced between $800 and $1,500. AGM batteries offer improved reliability and require less maintenance, but you will pay 15-25% more than standard types. Lithium batteries deliver premium performance, longer lifespan, and lighter weight, with prices ranging from $1,600 to over $6,000. Use the 12V Battery Types Comparison to match your needs with the right option.
Key Takeaways
- Choose STD lead-acid batteries for the lowest upfront cost and basic needs. They require regular maintenance but are reliable for starting power.
- AGM batteries offer a maintenance-free option with better performance than standard lead-acid. They are ideal for moderate deep cycling and provide improved safety.
- Select lithium batteries for premium performance and long lifespan. They excel in deep cycle applications and require minimal maintenance, making them a great long-term investment.
- Consider your specific needs, such as budget and application, when choosing a battery type. Each option has unique strengths that suit different scenarios.
- Always match your charger to the battery type to avoid damage. Using the wrong charger can lead to reduced lifespan and safety risks.
12v Battery Types Overview

When you explore 12v battery types, you encounter three main options: STD lead-acid, AGM, and lithium. Each type offers unique features that impact performance, maintenance, and suitability for different applications. Understanding these differences helps you select the right battery for your needs.
STD Lead-Acid Batteries
STD lead-acid batteries represent the most traditional choice among 12v battery types. You find these in many vehicles and backup power systems. They use lead dioxide for the cathode, sponge lead for the anode, and sulfuric acid as the electrolyte. The cells connect in series, and you can choose between a 12v flooded battery or a sealed design. These batteries deliver reliable starting power and handle high surge currents well. However, you must check water levels regularly and perform routine maintenance. Their energy density is lower than other 12v battery types, and they weigh more. You often select lead-acid for cost-sensitive projects or where deep cycling is not a priority.
| Battery Type | Chemical Composition | Structural Design | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lead-Acid | Lead dioxide (cathode), sponge lead (anode), sulfuric acid (electrolyte) | Cells connected in series, available in flooded and sealed designs | Reliable, robust, high surge currents |
AGM Batteries
AGM stands for Absorbed Glass Mat, a technology that improves on standard lead-acid designs. In AGM batteries, fiberglass mats absorb the acid, making the battery spill-proof and maintenance-free. This sealed structure means you do not need to add water or worry about leaks. AGM batteries fit well in deep cycle applications and offer better efficiency during charge and discharge cycles. You benefit from improved safety and longer service life compared to traditional lead-acid. AGM batteries weigh less than standard types but more than lithium. You often choose AGM when you need a balance of reliability, safety, and reduced maintenance in 12v battery types.
| Feature | AGM Battery | LiFePO4 Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Weight (Avg. 100Ah) | 60-70 lbs (27-32 kg) | 25-30 lbs (11-14 kg) |
| Energy Density | Lower | Higher |
| Cycle Life | 300 - 700 cycles | 3,000 - 7,000+ cycles |
Lithium Batteries
Lithium batteries, especially lithium-ion batteries, have changed the landscape of 12v battery types. These batteries use a graphite anode, a lithium compound cathode, and an electrolyte that moves lithium ions during charge and discharge. The sealed design prevents leaks and supports high energy density. You get a lightweight battery with a long cycle life—often thousands of cycles. Lithium batteries excel in deep cycle use, powering RVs, boats, and solar systems. You also benefit from fast charging, minimal maintenance, and consistent performance. Lithium-ion batteries cost more upfront, but you gain long-term value and reliability.
| Battery Type | Chemical Composition | Structural Design | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium-Ion | Graphite anode, lithium compound cathode, electrolyte facilitating ion movement | Sealed design preventing leakage, intercalation of lithium ions | High energy density, lightweight, long cycle life |
Tip: When you compare 12v battery types, consider your budget, required cycle life, and whether you need deep cycle performance. Each type offers strengths for specific scenarios.
How 12v Battery Types Work
STD Battery Structure
You find that a standard 12V lead-acid battery contains six individual cells. Each cell produces about 2 volts, and the cells connect in series to deliver the total 12 volts you need for most automotive and backup power applications. Inside each cell, you see lead dioxide plates (positive), sponge lead plates (negative), and a liquid sulfuric acid electrolyte. This design allows for chemical reactions that generate electrical energy. You must check the water level in these batteries and keep the terminals clean to ensure reliable operation. The open design means you need to handle them with care to avoid spills.
AGM Battery Structure
AGM batteries use a different approach. Instead of a free-flowing liquid, the electrolyte is absorbed into fiberglass mats. This structure gives you several advantages:
- The mats hold the acid in place, making the battery spill-proof.
- You get lower internal resistance, which means faster recharging and strong bursts of current for starting engines.
- The sealed design resists vibration and impact, so you see longer service life and less maintenance.
You do not need to add water or worry about leaks. The compact, sealed case also allows you to install AGM batteries in various positions, which adds flexibility for your projects.
Lithium Battery Structure
Lithium batteries use advanced chemistry and safety features. The most common types include Nickel Cobalt Aluminum (NCA), Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC), and Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4). Here is a quick comparison:
| Chemistry Type | Key Features | Safety Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| NCA | High energy, long life | Lower safety margin |
| NMC | High energy density | Higher risk of thermal instability |
| LiFePO4 | Long life, superior safety | High decomposition temperature, less prone to thermal instability |
You benefit from built-in Battery Management Systems (BMS) that monitor temperature and voltage. Many lithium batteries also include gas sensors and fire suppression systems for extra safety. The sealed design prevents leaks and supports high energy density, making these batteries ideal for deep cycle and high-performance uses.
Tip: Choose lithium batteries with LiFePO4 chemistry for the best balance of safety and lifespan.
Pros and Cons of 12v Battery Types
STD Battery Pros and Cons
When you evaluate standard lead-acid batteries, you notice several advantages and disadvantages. These batteries offer the lowest upfront cost among 12v battery types comparison options. You often choose them for budget-sensitive projects or where deep cycling is not a priority. Lead-acid batteries provide reliable starting power and handle high surge currents well, making them suitable for automotive and backup power systems.
However, you must perform regular maintenance. You need to check electrolyte levels and clean terminals to prevent corrosion. Lead-acid batteries are prone to leakage and swelling, especially if you overcharge or expose them to environmental stress. Common failure modes include thermal runaway, swelling, and leakage. Using the wrong charger can cause permanent damage.
Lead-acid batteries have a shorter cycle life compared to agm batteries and lithium batteries. You may need to replace them more frequently, which increases long-term costs. Safety risks include acid spills and gas emissions, so you must handle them with care. Warranty periods for lead-acid batteries are typically shorter than those for lithium-ion batteries.
Pros:
- Lowest upfront cost in 12v battery types comparison
- Reliable starting power and high surge current
- Widely available and compatible with most chargers
Cons:
- Requires regular maintenance (electrolyte top-ups, cleaning)
- Shorter cycle life than agm batteries and lithium batteries
- Prone to leakage, swelling, and environmental stress
- Higher safety risks (acid spills, gas emissions)
- Shorter warranty periods
AGM Battery Pros and Cons
AGM batteries represent an improvement over traditional lead-acid designs. You benefit from a sealed structure that eliminates the need for regular electrolyte top-ups. AGM batteries are spill-proof and maintenance-free, which reduces your workload. You still need to ensure proper venting and monitor charging to prevent overcharging, but overall maintenance is much lower than with standard lead-acid batteries.
In terms of performance, agm batteries deliver better efficiency during charge and discharge cycles. They offer a slightly longer life expectancy than standard lead-acid batteries, but you will need to replace them more often than lithium batteries. AGM batteries are less prone to catching fire and do not require specialized management systems.
Safety risks are lower compared to lead-acid batteries. AGM batteries resist vibration and impact, making them suitable for deep cycle applications and environments where reliability matters. However, agm batteries can suffer from diminished capacity in cold temperatures, especially when compared to lithium-ion batteries.
Warranty periods for agm batteries vary, but they are generally longer than those for standard lead-acid batteries and shorter than those for lithium batteries.
| Battery Type | Safety Risks | Management Systems |
|---|---|---|
| AGM | Less prone to catching fire | No specialized management required |
| Lithium | Requires sophisticated management to prevent overheating and fires | Yes |
Pros:
- Maintenance-free and spill-proof design
- Improved performance and efficiency over lead-acid batteries
- Longer cycle life than standard lead-acid batteries
- Lower safety risks (less prone to fire)
- Suitable for deep cycle and vibration-prone environments
Cons:
- Higher upfront cost than lead-acid batteries
- Shorter cycle life than lithium batteries
- Diminished capacity in cold temperatures
- Requires proper venting and charging monitoring
- Warranty periods shorter than lithium batteries
Lithium Battery Pros and Cons
Lithium batteries, especially lithium-ion batteries, set the standard for high performance battery options in the 12v battery types comparison. You experience premium performance, lightweight construction, and long cycle life. Lithium batteries excel in deep cycle applications, such as RVs, boats, and solar systems. You benefit from fast charging, minimal maintenance, and consistent output.
Lithium-ion batteries, particularly LiFePO4 models, are largely maintenance-free. They feature built-in battery management systems that prevent overcharging and monitor temperature and voltage. This advanced management reduces safety risks, although lithium batteries require sophisticated systems to prevent overheating and fires.
You notice that lithium batteries outperform agm batteries in extreme temperature conditions. At colder temperatures, lithium batteries retain more capacity than agm batteries, which lose performance quickly. Lithium batteries also offer the longest warranty periods, with some manufacturers providing up to 10 years of coverage.
Common failure modes for lithium batteries include thermal runaway, swelling, and charger mismatch. You must use compatible chargers to avoid permanent damage. Lithium batteries cost more upfront, but you gain long-term value through extended lifespan and reduced maintenance.
The results show that at colder temperatures all batteries exhibit some diminished capacity, but that the diminished capacity is much greater in an AGM battery versus a LiFePO4 battery, which only diminished slightly in capacity. The results of this study demonstrate that even though both AGM and LiFePO4 batteries are affected by low temperature discharges, the LiFePO4 batteries can perform significantly better than the AGM batteries.
Pros:
- Premium performance and high energy density
- Lightweight and compact design
- Maintenance-free with advanced battery management systems
- Longest cycle life and warranty periods in 12v battery types comparison
- Superior deep cycle capability and cold temperature performance
- Lower long-term cost due to extended lifespan
Cons:
- Highest upfront cost among 12v battery types
- Requires compatible chargers and management systems
- Potential safety risks if management systems fail
- Swelling and thermal runaway possible with improper use
Common Failure Modes for All Battery Types:
- Thermal Runaway: Excessive heat and potential fires or explosions
- Swelling and Leakage: Signs of degradation and safety hazards
- Environmental Stress: Punctures or moisture exposure compromise safety and performance
- Charger Mismatch: Overvoltage and permanent damage
Cycle Life Comparison:
- AGM batteries have a slightly longer life expectancy than standard lead-acid batteries.
- AGM batteries need to be replaced more often than lithium batteries.
- AGM batteries have a shorter cycle life compared to lithium batteries.
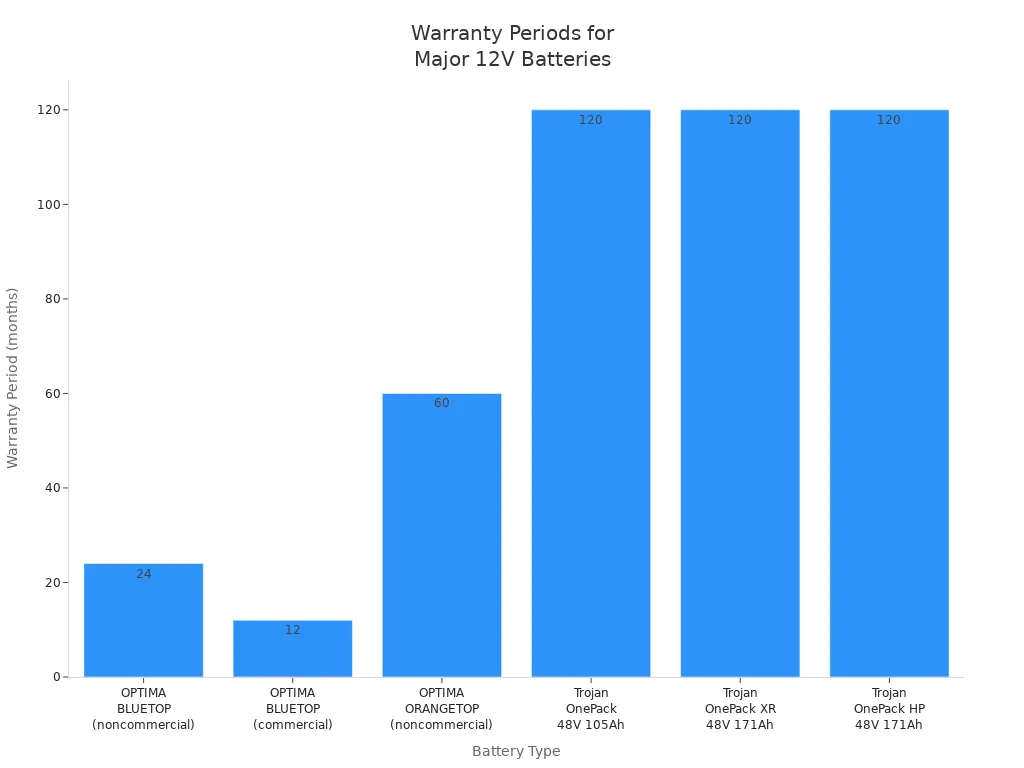
Warranty Comparison:
- OPTIMA BLUETOP Starting and Dual-Purpose Batteries: 24 months free replacement
- OPTIMA ORANGETOP Batteries: 60 months free replacement
- Trojan OnePack Lithium Batteries: 10 years (registration required)
Tip: When you compare 12v battery types, consider not just the upfront cost but also maintenance, cycle life, safety, and warranty coverage. Lithium batteries deliver the best long-term value, while agm batteries offer a balance of reliability and reduced maintenance. Lead-acid batteries remain the most affordable choice for basic needs.
12v Battery Types Comparison Table

Key Features Side-by-Side
When you compare 12v battery types, you need to see the numbers side by side. This helps you make a smart choice for your application. Below, you find a comprehensive table that highlights the most important specifications for standard lead-acid (STD), AGM, and lithium batteries. You see how each type performs in voltage, cycle life, and weight.
| Feature | STD Lead-Acid (Flooded) | AGM (Absorbed Glass Mat) | Lithium (LiFePO4) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fully Charged Voltage | 12.7 – 12.8V | 12.9 – 13.0V | 13.3 – 13.6V |
| Nominal Voltage | 12.6V | 12.7V | 12.8V |
| 50% Charge Voltage | 12.2V | 12.3V | 13.0V |
| Discharged Voltage (0%) | 11.9V | 11.9V | 10.0V |
| Cycle Life (Average) | 300 – 500 cycles | 500 – 800 cycles | 3,000 – 7,000+ cycles |
| Typical 100Ah Weight | 80 – 100 lbs | 60 – 80 lbs | 20 – 35 lbs |
| Maintenance | Regular (water, clean) | Maintenance-free | Maintenance-free |
| Deep Cycle Capability | Limited | Good | Excellent |
| Cold Temp. Performance | Moderate | Reduced | Superior |
| Safety Risks | Acid spills, gas | Low, sealed | Overheat (BMS protects) |
| Warranty | 1 – 2 years | 2 – 3 years | 5 – 10 years |
| Upfront Cost | $800 – $1,500 | $1,000 – $2,000 | $1,600 – $6,000+ |
Tip: You should always check the actual specifications from your battery manufacturer. These values represent typical ranges for each battery type.
? What Do These Numbers Mean for You?
- Voltage: Lithium batteries hold a higher voltage at every stage of charge. This means you get more consistent power for sensitive electronics.
- Cycle Life: If you want a battery that lasts for years, lithium stands out. You can expect thousands of cycles, while AGM and STD batteries need replacement much sooner.
- Weight: Lithium batteries weigh much less. You save space and reduce load, which matters for RVs, boats, and portable systems.
- Maintenance: You spend less time on lithium and AGM batteries. Standard lead-acid batteries require regular checks and water top-ups.
- Cold Weather: Lithium batteries perform better in cold conditions. AGM batteries lose capacity faster when temperatures drop.
⚡ Quick Comparison Checklist
- Choose STD Lead-Acid if you need the lowest upfront cost and do not mind regular maintenance.
- Pick AGM when you want a maintenance-free, reliable battery for moderate deep cycling.
- Go with Lithium for the best performance, lightest weight, and longest lifespan—even if the initial cost is higher.
Note: You should always match your charger to your battery type. Using the wrong charger can shorten battery life or cause safety issues.
By reviewing this table, you can quickly spot the strengths and weaknesses of each 12v battery type. This helps you select the right battery for your budget, performance needs, and long-term plans.
Choosing the Best 12v Battery Type
When to Choose STD
You should select STD lead-acid batteries when your priority is minimizing upfront costs. These batteries work well for basic automotive needs, emergency backup systems, and situations where deep cycling is not required. If you do not mind regular maintenance, such as checking water levels and cleaning terminals, lead-acid batteries provide reliable starting power. You find them compatible with most standard chargers, which makes replacement straightforward. Choose lead-acid if you need a widely available solution and do not plan to run high-drain accessories or deep cycle loads.
Note: Lead-acid batteries require consistent care. Neglecting maintenance can shorten their lifespan and increase safety risks.
When to Choose AGM
AGM batteries offer a balance between cost and durability. You benefit from a maintenance-free design, which eliminates the need for electrolyte top-ups. AGM batteries suit you if you want improved reliability and moderate deep cycle capability. These batteries perform well for occasional riders, UTVs, and vehicles with moderate accessory loads. AGM batteries are heavier and have a shorter lifespan compared to lithium-ion batteries, but they remain more affordable. If you value durability and do not want to worry about leaks or spills, AGM is a strong choice.
- AGM batteries are more cost-effective and durable for occasional use.
- You should use trickle chargers to keep AGM batteries in optimal condition.
- For those running multiple accessories, consider a dual battery kit for added reliability.
When to Choose Lithium
Lithium batteries deliver superior performance, long lifespan, and minimal weight. You should choose lithium if you need sustained power for high-drain applications, such as RVs, marine systems, and solar setups. Lithium-ion batteries, especially Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4), excel in deep cycle scenarios and provide thousands of cycles with minimal maintenance. These batteries retain capacity in cold temperatures and offer the longest warranty periods. Although lithium batteries cost more initially, you gain long-term value through extended service life and reduced maintenance.
- Deep cycle lithium batteries are ideal for RVs and marine use.
- Lithium-ion batteries minimize weight and maximize battery life.
- Choose lithium when you want premium performance and reliability for demanding applications.
Tip: Always match your charger to the battery type. Using an incompatible charger can damage lithium-ion batteries and reduce their lifespan.
Compatibility and Replacement Tips
AGM vs STD Replacement
When you replace a lead-acid battery with an AGM battery, you gain several benefits. AGM batteries fit most applications that use standard lead-acid batteries. You do not need to change wiring or mounting hardware. However, you must check your charger settings. AGM batteries do not tolerate the equalization stage used for flooded lead-acid batteries. This stage can damage lithium-ion batteries and shorten AGM battery life.
| Consideration | Details |
|---|---|
| AGM Settings | Not suitable for lithium-ion batteries due to equalization stage |
| User Charge Profile | Adjust charge voltage to around 55V and observe for necessary adjustments |
Tip: Always review your charger’s manual before switching battery types. Incorrect settings can reduce battery lifespan.
Charger Compatibility
You must select a charger that matches your battery type. Not all chargers work with lithium-ion batteries. Many AGM chargers do not provide the correct voltage for lithium-ion batteries. Lithium-ion batteries require a charging voltage between 14.2V and 14.6V. These batteries do not need float charging, which prevents overcharging.
Recommended steps for charger compatibility:
- Ensure your charger has a 'Lithium Mode' or allows manual voltage adjustment.
- Set the charging voltage to 14.2V – 14.6V for a 12V system.
- Avoid float charging to protect lithium-ion batteries.
| Charger Model | Amperage | Battery Types Compatible | Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| NOCO Genius 10 | 10 Amp | AGM, lithium-ion batteries, lead-acid, Gel | Dual Voltage, Intrusion Protected |
| NOCO Genius 5 | 5 Amp | AGM, lithium-ion batteries, lead-acid, Gel | Intrusion Protected, Ideal for 120 AH |
- Chargers with higher amperage recharge batteries quickly.
- Low current chargers maintain batteries during off-seasons.
- Multi-bank chargers allow you to charge several batteries at once.
Note: Using the wrong charger for lead-acid or lithium-ion batteries can cause permanent damage. Always confirm compatibility before connecting.
Identifying 12v Battery Types
Physical Features
You can identify 12V battery types by examining their physical characteristics. Each type has unique features that help you distinguish them quickly. Use the table below to compare standard (STD), AGM, and lithium batteries:
| Feature | STD Battery | AGM Battery | Lithium Battery |
|---|---|---|---|
| Design | Liquid electrolyte, vent caps, can spill | Absorbed electrolyte, flat or spiral cells, sealed | Sealed case, compact, no vent caps |
| Maintenance | Water top-ups required, exposed plates | Maintenance-free, no water needed | Maintenance-free, integrated BMS |
| Weight | Heavier, thick casing | Lighter than STD, robust shell | Lightest, slim profile |
| Spill Resistance | Can leak if tipped or damaged | Spill-proof, can mount in any position | Fully sealed, no risk of leaks |
| Durability | Prone to vibration damage | Shock-resistant, handles vibration | Highly durable, resists vibration |
| Temperature Range | Sensitive to extreme temperatures | Performs better in cold and heat | Excellent performance in all temps |
You notice that STD batteries often have removable vent caps and a heavier build. AGM batteries feature sealed tops and a more rugged case. Lithium batteries stand out with their lightweight, compact design and lack of vent caps.
Tip: Always check for vent caps and battery weight. These clues help you identify the type at a glance.
Labeling and Identification
You should always read the label on the battery case. Manufacturers print important information directly on the battery. Look for these details:
- Battery Type: Labels often state "Flooded," "AGM," or "Lithium" (sometimes "LiFePO4" or "LFP").
- Model Number: Many model numbers include hints, such as "AGM" or "LFP."
- Voltage and Capacity: Check for "12V" and the amp-hour (Ah) rating.
- Certifications: Look for safety marks and recycling symbols.
- Date Code: Find the manufacturing or expiration date for warranty tracking.
If you see a sealed case with no vent caps and a label that mentions "AGM," you hold an AGM battery. If the label says "LiFePO4" or "Lithium," you have a lithium battery. STD batteries usually have vent caps and may say "Flooded" or "Lead-Acid."
Note: If you cannot find clear labeling, consult the owner's manual or contact the manufacturer. Proper identification ensures you use the correct charger and maintenance routine.
By checking both physical features and labels, you can confidently identify any 12V battery type and avoid costly mistakes.
You see clear differences among 12V battery types. STD and AGM batteries offer reliability for basic and moderate needs, while lithium batteries prov
-
 May.2026.02.27Lithium-Ion Batteries: The Six Constraints Blocking the Path to PerfectionLearn More
May.2026.02.27Lithium-Ion Batteries: The Six Constraints Blocking the Path to PerfectionLearn More -

 May.2026.02.25Li-Polymer Battery 5000mAh: Complete Technical & OEM GuideLearn More
May.2026.02.25Li-Polymer Battery 5000mAh: Complete Technical & OEM GuideLearn More -
 May.2026.02.24The Unparalleled Advantages of Lithium-Ion Batteries Over Traditional BatteriesLearn More
May.2026.02.24The Unparalleled Advantages of Lithium-Ion Batteries Over Traditional BatteriesLearn More -
 May.2026.02.243.6 Volt Battery: Complete Technical Guide for Engineers & BuyersLearn More
May.2026.02.243.6 Volt Battery: Complete Technical Guide for Engineers & BuyersLearn More -
 May.2026.02.24What Is a 3.8V LiPo Battery? A Complete Engineering & OEM GuideLearn More
May.2026.02.24What Is a 3.8V LiPo Battery? A Complete Engineering & OEM GuideLearn More