What is battery storage and how does it work
You use battery storage to hold electrical energy and release it when you need power. Battery energy storage systems store energy by converting electricity into chemical energy inside the battery. When you need power, the battery reverses the process and supplies electricity. These systems play a vital role in supporting renewable energy and keeping the power grid stable.
- Batteries help balance supply and demand by providing frequency regulation, voltage support, and load shifting.
- They store extra energy from renewable sources and release it during peak times, ensuring a reliable supply.
Key Takeaways
- Battery storage systems convert electricity into chemical energy for later use, helping you manage energy needs efficiently.
- You can save money by charging batteries during off-peak hours and using stored energy during peak demand times.
- Understanding the different battery technologies, like lithium-ion and lead-acid, helps you choose the best option for your needs.
- Regular maintenance of your battery system ensures safety and extends its lifespan, allowing for reliable energy storage.
- Using battery storage supports renewable energy integration, reduces reliance on fossil fuels, and contributes to a cleaner environment.
Battery Storage Basics

What is Battery Storage
You rely on battery storage to manage your energy needs more efficiently. This technology allows you to store electricity when supply is high or demand is low, then use it when you need power most. Battery storage systems convert electrical energy into chemical energy inside the battery. When you require electricity, the system reverses the process and delivers energy back to your home, business, or the grid.
Battery storage plays several important roles in modern energy systems. You can use it to balance supply and demand, especially when renewable sources like solar or wind fluctuate. These systems respond quickly to changes in energy demand, acting as a buffer to keep your power supply consistent. You benefit from reliable energy during peak consumption periods and when renewable generation drops.
Tip: Battery storage helps you maximise the use of renewable energy and reduce your reliance on fossil fuels.
Here are the main functions of battery storage in energy systems:
- Manage electricity demand and generation changes.
- Store energy during high supply periods for later use.
- Smooth out intermittency in renewable energy generation.
You also gain advantages such as energy independence, cost savings, and reduced carbon emissions. The table below summarises these benefits:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Energy Independence | Reduces reliance on the grid, enhancing resilience to outages. |
| Cost Savings | Enables you to store energy at lower rates and use it during peak times, lowering costs. |
| Grid Support | Provides support during peak demand, stabilising the grid and minimising infrastructure needs. |
| Environmental Impact | Maximises renewable energy use, reducing fossil fuel reliance and promoting cleaner energy. |
Key Components
You need to understand the essential components that make up a battery energy storage system. Each part plays a specific role in storing and delivering energy safely and efficiently.
- Battery Modules: These house individual battery cells and convert chemical energy to electrical energy. You depend on them for the actual storage and release of energy.
- Storage Enclosure: This provides a safe and controlled environment for the battery modules, protecting them from external hazards.
- Power Conversion System (PCS): You use this to convert direct current (DC) from the battery into alternating current (AC) for use in your home, business, or the grid.
- Battery Management System (BMS): This monitors and ensures safe operation of the battery cells by tracking current, voltage, and temperature.
- Energy Management System (EMS): You rely on this system to manage and optimise energy flow within the battery storage setup.
- Thermal Management Systems: These maintain optimal operating temperatures, ensuring safety and efficiency.
- Safety Systems: Fire suppression and monitoring systems protect you and your property by preventing and responding to potential hazards.
Note: A well-designed battery storage system combines all these components to deliver reliable, safe, and efficient energy storage for your needs.
You can see how each part works together to help you store energy, manage supply and demand, and support renewable integration. By understanding these basics, you make informed decisions about using battery storage in your home or business.
How Battery Energy Storage Systems Work
Charging and Discharging
You rely on a battery energy storage system to manage the flow of energy between your power sources and your needs. The process begins with charging, where you direct surplus electricity—often from solar panels or the grid—into the battery. This happens when energy production exceeds your immediate consumption. The system converts this electrical energy into a chemical form, storing it safely until you need it.
When demand rises or renewable generation drops, you trigger the discharging process. The battery energy storage system releases the stored energy, converting it back into electricity for your appliances, business, or the grid. Advanced control systems constantly monitor your energy production, consumption patterns, and battery status. These systems optimise charging and discharging to maximise efficiency and battery lifespan.
- Charging Process: You transfer electricity from sources like solar panels or the grid to the battery during periods of surplus. The system stores this energy in a chemical form.
- Discharging Process: When your demand exceeds supply, the battery releases stored energy, converting it back into electricity for use.
- Management: Control systems analyse your energy needs and battery condition, adjusting charging and discharging cycles for optimal performance.
The operation of a battery energy storage system involves several key steps:
- The Power Conversion System (PCS) draws in AC power from the grid or renewable sources and converts it into DC for storage in the battery.
- The battery stores the converted DC power until you need it.
- When demand increases, the PCS converts the stored DC power back into AC, supplying it to your appliances or the grid.
You benefit from this process by balancing supply and demand, reducing your reliance on the grid during peak times, and making the most of renewable energy.
Tip: By storing energy when it is abundant and releasing it during peak demand, you can lower your energy costs and increase your energy independence.
The efficiency of charging and discharging cycles depends on several factors. Temperature plays a significant role in battery performance and lifespan. The table below shows how different temperature conditions affect your battery energy storage system:
| Temperature Condition | Effect on Battery | Impact on Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| High Temperatures | Accelerated degradation risks | Reduced lifespan by up to 20% |
| Low Temperatures | Reduced capacity and charge acceptance | Loss of up to 40% usable energy below freezing |
You should also consider the depth of discharge (DoD), which indicates the percentage of battery capacity used. Different battery chemistries have varying DoD thresholds, and optimising DoD can extend battery life by up to 25%. The method of charging matters as well. Pulse charging, for example, reduces heat generation and improves charge acceptance, potentially extending battery lifespan by an average of 15%.
Chemical to Electrical Energy
You experience the core function of a battery energy storage system through the conversion of energy between chemical and electrical forms. This process happens in two main stages:
- Charging: You supply electrical energy to the battery. Inside, chemical reactions store this energy in a stable form.
- Discharging: When you need power, the battery reverses these chemical reactions, releasing the stored energy as electricity.
The battery management system (BMS) and energy management system (EMS) work together to monitor and control these conversions. The BMS tracks the health and status of each battery cell, while the EMS ensures that energy flows efficiently between your sources, storage, and loads.
You depend on this seamless conversion to keep your lights on, your business running, and your renewable energy working for you. The ability to store and release energy on demand allows you to balance supply and demand, support the grid, and reduce your environmental impact.
Note: Battery energy storage systems give you the flexibility to use energy when you need it most, making your energy use smarter and more sustainable.
By understanding how charging, discharging, and energy conversion work, you can make informed decisions about integrating battery storage into your home or business. You gain control over your energy use, improve efficiency, and support a cleaner energy future.
Types of Battery Energy Storage System

You have several options when choosing a battery technology for energy storage. Each type offers unique benefits and limitations, making it important to match the right solution to your needs.
Lithium-Ion
Lithium-ion batteries dominate the battery storage market worldwide. You find them in everything from home systems to large-scale grid projects. This battery technology delivers high energy density, long service life (up to 3,000 cycles), and low self-discharge. You benefit from their lightweight design and minimal maintenance requirements. However, you should consider the higher upfront cost and the increased fire risk if the battery is damaged or mishandled. Environmental concerns also arise from the extraction and disposal of raw materials.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Wide range of applications | Fire hazard |
| Long service life (up to 3,000 cycles) | Temperature sensitivity |
| High current capability | Low environmental compatibility in raw material extraction |
| High energy density | Disposal and recycling issues |
| Low self-discharge | Cost (more expensive than other battery types) |
| No memory effect | Increased fire risk if damaged or mishandled |
Note: You should always follow manufacturer guidelines to ensure safe operation of lithium-ion battery technology.
Lead-Acid
Lead-acid batteries represent a traditional battery technology that you still find in many stationary energy storage applications. They offer lower initial costs and high recyclability. However, you must perform regular maintenance, and the batteries are heavy and less efficient than lithium-ion options. Their lifespan is shorter, which can lead to higher long-term costs due to replacements.
| Feature | Lead-Acid Batteries | Lithium-Ion Batteries |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Lower upfront costs | Higher upfront costs |
| Maintenance Requirements | More demanding maintenance | Reduced maintenance needs |
| Lifespan | Shorter lifespan | Longer lifespan |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower energy efficiency | Higher energy efficiency |
| Long-term Costs | Potentially higher due to replacements | Lower due to longevity and efficiency |
Other Technologies
You can also explore emerging battery technology for energy storage. Sodium-ion, solid-state, flow, lithium-sulphur, zinc-air, and iron-air batteries are gaining attention for large-scale projects. Flow batteries, for example, allow you to scale energy capacity by increasing the size of electrolyte tanks, making them ideal for grid support. Sodium-ion batteries offer lower costs and compatibility with existing systems, but they have lower energy density than lithium-ion.
| Technology | Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium-ion | Lower costs, compatibility with lead-acid systems | Lower energy density, limited commercial interest |
| Flow batteries | Scalability, ideal for stationary grid use, proven vanadium chemistry | High costs, material dependencies, environmental concerns |
Tip: You may see more of these battery storage technologies in the future as research and development continue.
Pros and Cons
You need to weigh the pros and cons of each battery technology before making a decision.
| Battery Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Lithium-Ion | Lightweight, high efficiency, long lifespan | Higher upfront cost, environmental impact, safety concerns |
| Lead-Acid | Cost-effective, high recyclability | Heavy, requires maintenance, lower efficiency |
| Portable Stations | Convenient, easy to use | Limited capacity, not for long-term needs |
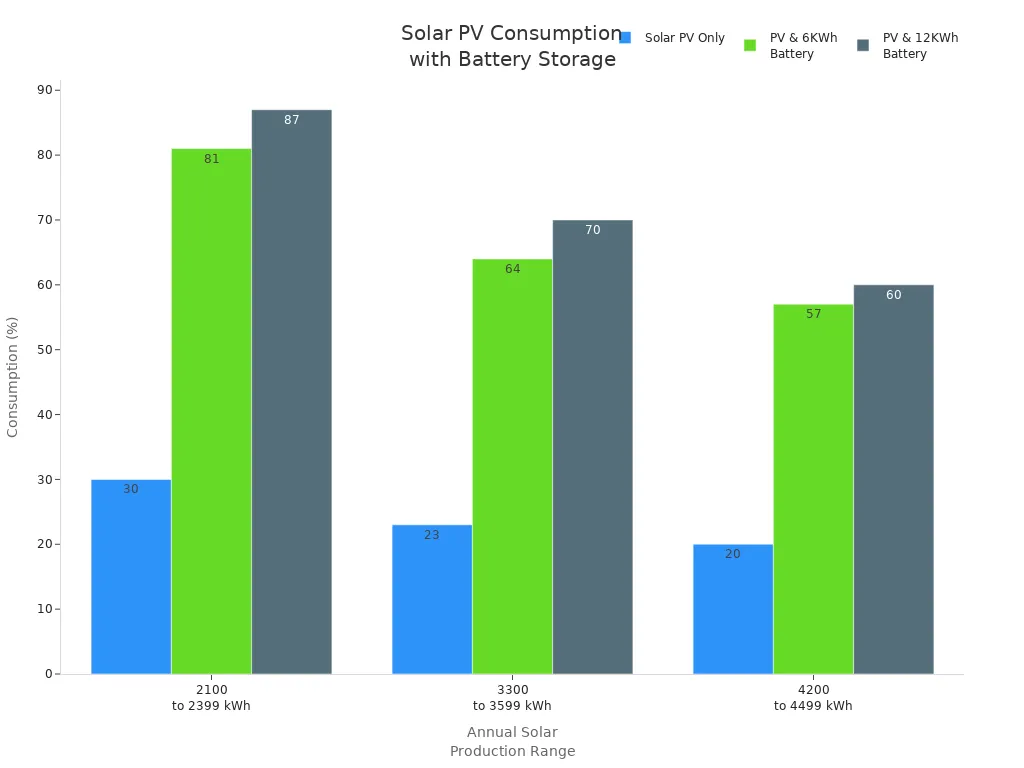
You can see that battery storage increases your solar energy consumption significantly. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each battery technology, you make informed choices that suit your energy needs and budget.
Energy Storage Applications
Home and Business Use
You can use energy storage in your home or business to optimise how you consume and manage electricity. Battery storage allows you to store surplus energy from renewable sources such as solar panels or wind turbines. You gain energy independence and backup power during outages. In commercial settings, battery energy storage solutions help you reduce reliance on the grid and lower costs through peak shaving and load shifting.
- Store excess energy from renewables for later use.
- Use stored energy during peak demand to avoid high tariffs.
- Achieve backup power during grid outages.
- Optimise energy use and reduce demand charges.
You can charge batteries during off-peak hours when electricity is cheaper and discharge them during peak times. This strategy leads to significant savings. For example, a 10-kWh battery system can save you up to £589 per year, while a larger 20-kWh system could save £1,179 annually.
Renewable Integration
Energy storage plays a vital role in renewable energy integration. You can smooth out the variability of solar and wind power by storing excess energy when production is high and using it when output drops. This approach ensures a steady supply and maximises your use of clean energy.
- Fill gaps when solar or wind output fluctuates.
- Use stored renewable energy during peak demand or high grid prices.
- Reduce your dependence on fossil fuels and lower emissions.
Battery energy storage systems help you increase on-site electricity usage by up to 75%, which further reduces your need to buy electricity from suppliers.
Grid Support
You support the wider electricity grid by using battery energy storage solutions. These systems provide rapid-response services such as frequency regulation and voltage support. They absorb excess energy during periods of high generation and release it when demand rises, helping to stabilise the grid.
- Manage supply and demand effectively.
- Prevent overloads and ensure grid stability.
- Integrate more renewable energy into the grid.
Grid operators face challenges such as unpredictable storage performance and lengthy interconnection queues. Improved visibility and clear policies are needed to support wider integration.
Benefits and Drawbacks
You benefit from energy storage through cost savings, energy independence, and improved reliability. However, you must consider initial costs and maintenance needs. The table below summarises the main advantages and disadvantages for different users:
| User Group | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Homeowners | Cost savings, energy independence, backup power | Initial costs, maintenance issues |
| Businesses | Lower costs, income from grid services | Initial costs, maintenance issues |
| Utilities | Grid stability, peak load management | Initial costs, regulatory hurdles |
Note: Combining battery storage with renewable energy can reduce your energy bills by up to 85% and cut carbon emissions by 45 tonnes over the system’s lifetime.
Lifespan and Environmental Impact
System Lifespan
You need to consider how long your battery storage system will last before investing. The average lifespan depends on the battery technology you choose:
- Lithium-ion: 10 to 15 years
- Lead-acid: 3 to 5 years
- Flow batteries: around 10 to 20 years
- Sodium-sulfur: up to 15 years
The table below gives you a quick comparison:
| Battery Type | Average Lifespan | Typical Warranty |
|---|---|---|
| Lithium-Ion | 10–15 years | 10 years |
| Lead-Acid | 3–5 years | 2–5 years |
| Flow Batteries | 10–20 years | Varies |
You can extend the life of your energy storage system by managing temperature, avoiding deep discharges, and choosing the right chemistry for your needs. High temperatures and frequent deep discharges reduce battery life. Install your system in a cool, well-ventilated area to prevent premature degradation.
Maintenance Needs
You must maintain your battery storage system to ensure safety and performance. Regular maintenance includes:
- Monthly visual inspections for wear, tear, and correct voltage.
- Quarterly cleaning to prevent dust and corrosion.
- Yearly professional testing to catch potential issues early.
Lead-acid batteries require more attention. You need to check fluid levels, add distilled water, and clean terminals regularly. Lithium-ion batteries are almost maintenance-free, saving you time and reducing system costs.
Professional electricians use tools like multimeters and thermal cameras to inspect your battery system and ensure safe operation.
Environmental Considerations
You should understand the environmental impact of energy storage across its lifecycle. The main stages include production, transportation, installation, operation, maintenance, and end-of-life disposal or recycling.
| Stage | Description | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Battery Production | Manufacturing cells and modules | High greenhouse gas emissions |
| Transportation | Shipping to installation sites | Increased carbon footprint |
| Installation | Setting up infrastructure | Moderate resource use |
| Operation | Storing and releasing energy | Depends on energy mix and energy efficiency |
| Maintenance | Repairs and part replacements | Resource and energy use |
| End of Life | Disposal or recycling | Hazardous waste risk; recycling reduces raw material need |
You can reduce negative impacts by recycling batteries and choosing systems with longer lifespans. Proper disposal and recycling help recover valuable materials and lower the demand for new resources.
You have seen how battery storage lets you store and use electricity when you need it most. A battery energy storage system gives you control over your power supply and helps you make the most of renewable energy. You can reduce costs, improve reliability, and support a cleaner future. Consider how a battery could benefit your home or business. Take the next step towards smarter energy use.
-
 May.2026.02.27Lithium-Ion Batteries: The Six Constraints Blocking the Path to PerfectionLearn More
May.2026.02.27Lithium-Ion Batteries: The Six Constraints Blocking the Path to PerfectionLearn More -

 May.2026.02.25Li-Polymer Battery 5000mAh: Complete Technical & OEM GuideLearn More
May.2026.02.25Li-Polymer Battery 5000mAh: Complete Technical & OEM GuideLearn More -
 May.2026.02.24The Unparalleled Advantages of Lithium-Ion Batteries Over Traditional BatteriesLearn More
May.2026.02.24The Unparalleled Advantages of Lithium-Ion Batteries Over Traditional BatteriesLearn More -
 May.2026.02.243.6 Volt Battery: Complete Technical Guide for Engineers & BuyersLearn More
May.2026.02.243.6 Volt Battery: Complete Technical Guide for Engineers & BuyersLearn More -
 May.2026.02.24What Is a 3.8V LiPo Battery? A Complete Engineering & OEM GuideLearn More
May.2026.02.24What Is a 3.8V LiPo Battery? A Complete Engineering & OEM GuideLearn More