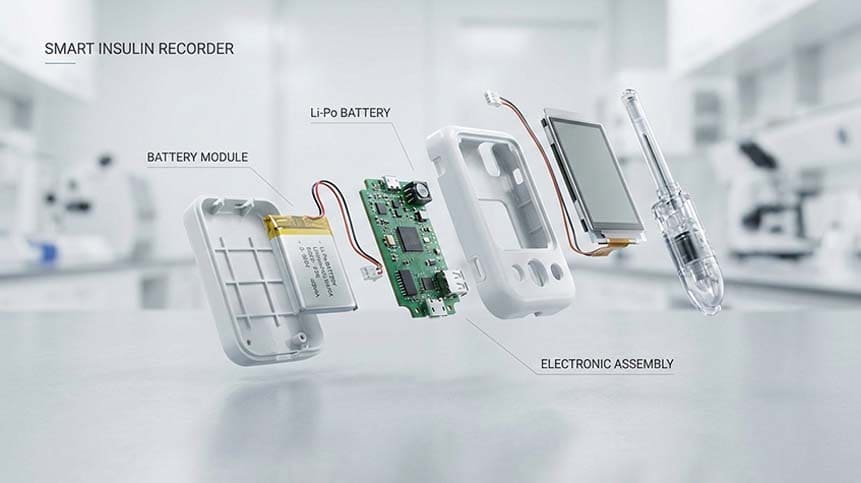
Smart Insulin Recorder Battery: Powering Accurate Diabetes Management Devices

Introduction: Why the Battery Matters in Smart Insulin Recorders
As professionals working closely with medical device manufacturers, we see a clear trend: smart insulin recorders and connected insulin pens are becoming core tools in diabetes management.
These devices don’t just log injections—they synchronize data, enable clinical insights, and support regulatory-grade accuracy. At the heart of all this functionality lies a component that is often underestimated but critically important:
the smart insulin recorder battery.
A battery failure does not simply mean downtime—it risks data loss, inaccurate dosing records, and regulatory non-compliance. That’s why battery selection for insulin recording devices must be approached as a medical engineering decision, not a consumer electronics afterthought.
What Is a Smart Insulin Recorder?
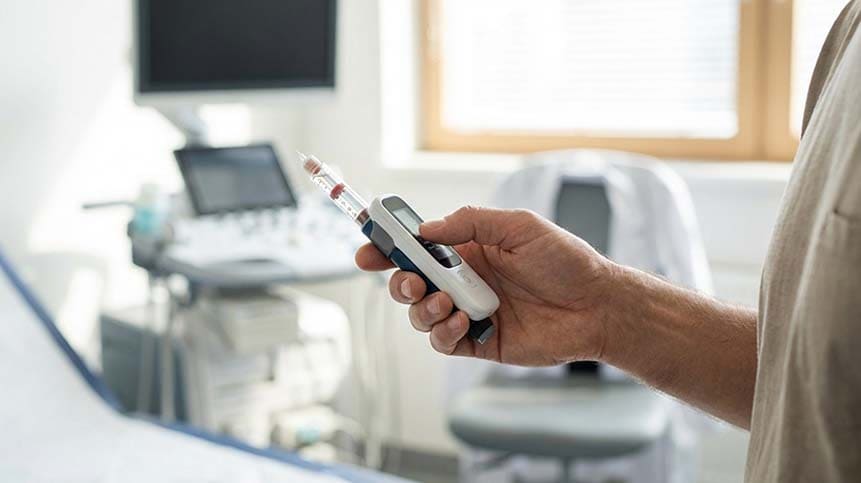
A smart insulin recorder is a compact electronic module integrated into or attached to an insulin pen or injector. Its primary functions include:
-
Recording injection time and dosage
-
Storing historical insulin usage data
-
Transmitting data via Bluetooth or NFC
-
Synchronizing with mobile apps or cloud platforms
Most smart insulin recorders are classified as Class I or Class II medical devices, depending on region and function, which directly impacts battery requirements.
Core Battery Requirements for Smart Insulin Recorders
From our experience supplying batteries for medical OEMs, insulin recorder batteries must meet five non-negotiable criteria:
1. Ultra-Low Power Consumption Support
Smart insulin recorders typically operate in deep sleep mode over 95% of the time, waking only to:
-
Detect injection motion
-
Log dosage data
-
Transmit data periodically
The battery must support stable voltage at microamp-level current draw, something many standard consumer batteries fail to do reliably.
2. Long Operational Life (12–36 Months)
Most insulin recorders are sealed, non-user-replaceable devices. Battery life expectations include:
| Device Type | Expected Battery Life |
|---|---|
| Basic insulin recorder | 12–18 months |
| Bluetooth-enabled recorder | 18–24 months |
| Cloud-connected recorder | 24–36 months |
A short battery lifespan increases:
-
Warranty claims
-
Device returns
-
Regulatory risk
3. Medical-Grade Safety and Stability
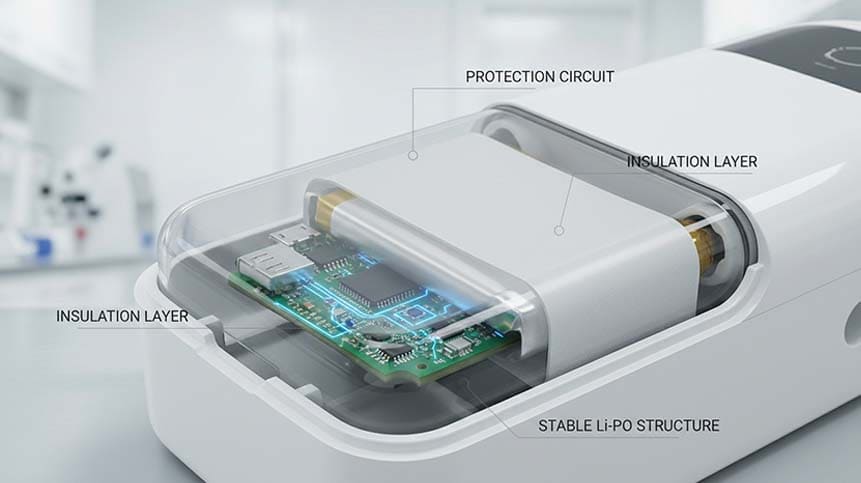
Because insulin recorders are used daily, often by elderly or pediatric patients, the battery must offer:
-
No leakage risk
-
Excellent thermal stability
-
Resistance to over-discharge
Lithium chemistry selection is critical here.
4. Compact Form Factor
Smart insulin recorders demand:
-
Thin profiles
-
Custom shapes (curved, ultra-slim)
-
Lightweight design (<5g battery mass)
This rules out many standard cylindrical cells.
5. Regulatory & Compliance Readiness
Battery materials and structure must support compliance with:
-
IEC 62133
-
UN38.3
-
ISO 10993 (biocompatibility, when applicable)
-
FDA / MDR technical documentation
Common Battery Types Used in Smart Insulin Recorders
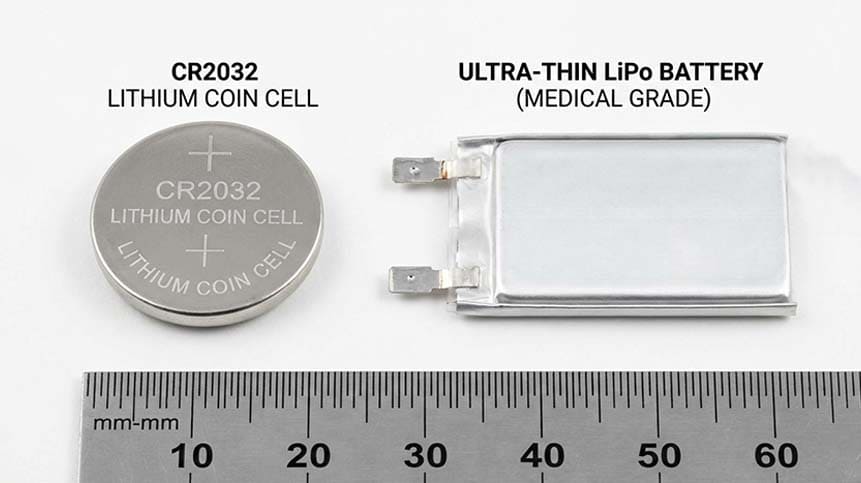
Lithium Primary Coin Cells (CR Series)
Pros:
-
Extremely low self-discharge
-
Long shelf life (5–10 years)
-
Simple power management
Cons:
-
Limited current output
-
Not rechargeable
Typical use case:
Basic insulin recorders without wireless communication.
Lithium Polymer (LiPo) Rechargeable Batteries
Pros:
-
Ultra-thin and customizable
-
Supports Bluetooth transmission
-
Rechargeable design
Cons:
-
Requires protection circuitry
-
Shorter total lifecycle vs primary lithium
Typical use case:
Smart insulin pens and Bluetooth-enabled recorders.
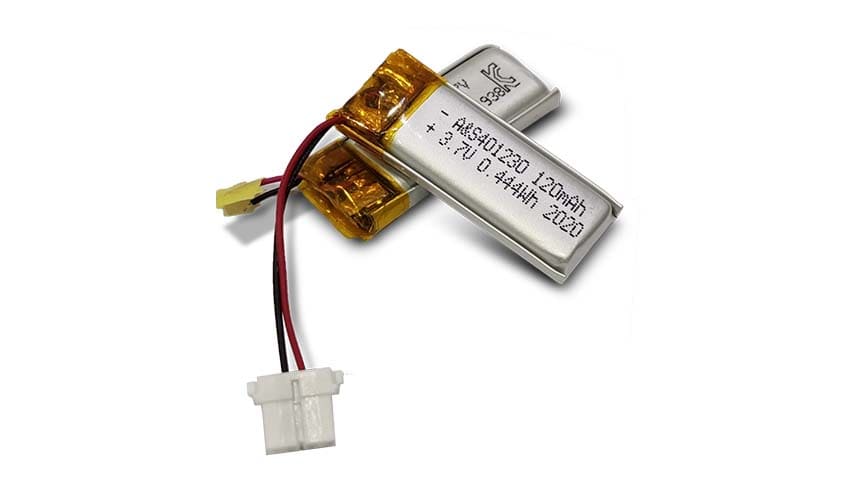
AS401230 3.7V 120mAh Lithium Polymer Battery with UL1642/CB/UN38.3/CE/KC certification For use with smart insulin recorders.
Lithium Manganese Dioxide (Li-MnO₂)
Often overlooked but increasingly popular in medical wearables.
Key advantages:
-
High energy density
-
Excellent voltage stability
-
Strong safety profile
Battery Capacity vs Power Consumption: Real-World Data
Below is a simplified power consumption breakdown based on industry averages:
| Function | Current Draw | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Sleep mode | 2–5 µA | 23+ hours/day |
| Injection detection | 3–8 mA | <1 second |
| Bluetooth transmission | 10–15 mA | <5 seconds/day |
Insight:
Battery optimization is less about “large capacity” and more about efficient power management.
Safety Considerations for Diabetes Device Batteries
From a compliance standpoint, insulin recorder batteries must address:
-
Overcharge protection
-
Over-discharge protection
-
Short-circuit prevention
-
Mechanical integrity under daily handling
In our projects, we often integrate:
-
Dual-layer protection circuits
-
Medical-grade insulation materials
-
Laser-welded tabs for reliability
Custom Battery Solutions for Smart Insulin Recorders
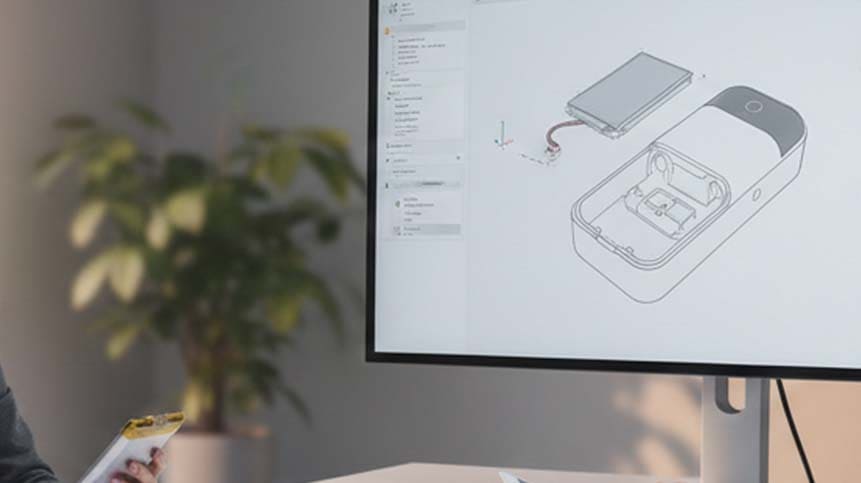

Off-the-shelf batteries rarely fit medical device constraints perfectly.
When Customization Is Necessary
Custom battery solutions are recommended when:
-
Device thickness <5 mm
-
Non-rectangular housing
-
Specific voltage cut-off requirements
-
Long standby + burst transmission profile
Customization Options
| Custom Parameter | Available Options |
|---|---|
| Shape | Rectangular, curved, L-shape |
| Thickness | As thin as 2.5 mm |
| Capacity | 20 mAh – 500 mAh |
| Connector | FPC, JST, welded tabs |
| Protection | Single / dual IC |
Battery Testing & Validation in Medical Applications
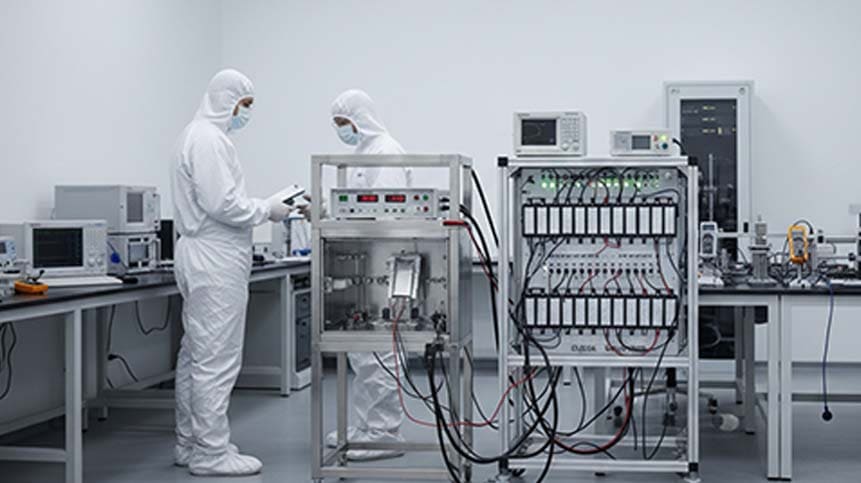

Before mass production, insulin recorder batteries typically undergo:
-
Cycle life testing
-
Shelf aging simulation
-
Temperature stress tests (-20°C to +60°C)
-
Transportation simulation (UN38.3)
This testing data is often included in technical files for FDA or MDR submissions.
Regulatory Landscape: What OEMs Must Consider
United States
-
FDA 21 CFR Part 820
-
Battery documentation included in Design History File (DHF)
European Union
-
MDR (EU 2017/745)
-
Battery traceability and material disclosure required
Global Transport
-
UN38.3 certification mandatory
Why Battery Reliability Impacts Clinical Trust
A smart insulin recorder is only as reliable as its power source.
Battery-related failures can lead to:
-
Missing insulin dose records
-
App synchronization errors
-
Loss of patient confidence
For chronic disease management, trust equals adherence, and adherence starts with device reliability.
References
Related articles:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What battery is commonly used in smart insulin recorders?
Most smart insulin recorders use lithium primary coin cells or ultra-thin lithium polymer batteries, depending on whether wireless connectivity is required.
How long does a smart insulin recorder battery last?
Battery life typically ranges from 12 to 36 months, depending on transmission frequency, sensor activity, and power management design.
Are smart insulin recorder batteries replaceable?
Most are sealed and non-user-replaceable to maintain device integrity and regulatory compliance.
Do insulin recorder batteries need medical certification?
Yes. Batteries must support device compliance with IEC 62133, UN38.3, and relevant FDA or MDR requirements.
-
 May.2026.02.27Lithium-Ion Batteries: The Six Constraints Blocking the Path to PerfectionLearn More
May.2026.02.27Lithium-Ion Batteries: The Six Constraints Blocking the Path to PerfectionLearn More -

 May.2026.02.25Li-Polymer Battery 5000mAh: Complete Technical & OEM GuideLearn More
May.2026.02.25Li-Polymer Battery 5000mAh: Complete Technical & OEM GuideLearn More -
 May.2026.02.24The Unparalleled Advantages of Lithium-Ion Batteries Over Traditional BatteriesLearn More
May.2026.02.24The Unparalleled Advantages of Lithium-Ion Batteries Over Traditional BatteriesLearn More -
 May.2026.02.243.6 Volt Battery: Complete Technical Guide for Engineers & BuyersLearn More
May.2026.02.243.6 Volt Battery: Complete Technical Guide for Engineers & BuyersLearn More -
 May.2026.02.24What Is a 3.8V LiPo Battery? A Complete Engineering & OEM GuideLearn More
May.2026.02.24What Is a 3.8V LiPo Battery? A Complete Engineering & OEM GuideLearn More
















