The advantage and disadvantage of lithium ion battery
When you pick a lithium ion battery for your phone, laptop, or car, you think about some important things. Lithium-ion batteries hold a lot of energy, charge quickly, and last a long time. This makes them common in electronics and vehicles. But they can cost more, have safety risks, and need special storage.
Advantages:
- Light weight
- Lasts a long time
- Needs little care
- Charges quickly
Disadvantages:
- Costs a lot to make
- Can be harmed by heat or cold
- Must be handled with care
Key Takeaways
- Lithium-ion batteries are light and store lots of energy. This lets devices be small and work longer before charging.
- These batteries charge fast. Phones can get 50-70% power in less than 30 minutes. This is good for people who are busy.
- Lithium-ion batteries last a long time. But they cost a lot to make. They need to be handled with care to stay safe.
- Battery performance changes with temperature. Keeping batteries at safe temperatures helps them last longer.
- Think about price, safety, and the environment when picking a lithium-ion battery for your devices.
Advantages of lithium-ion battery

High energy density
Lithium-ion batteries can hold a lot of energy. They fit more power into a small space. This helps your phone or laptop last longer.
- Most lithium-ion batteries store between 150 and 300 Wh/kg.
- New models can go over 250 Wh/kg. Future batteries may hold even more.
- Nickel-metal hydride and lead-acid batteries have less energy density.
- More energy density means lighter devices and longer use.
- You get small and light electronics that are easy to carry.
Tip: High energy density is a big reason why lithium-ion batteries are popular. It lets you use your devices longer and makes them easier to move.
Long cycle life
Lithium-ion batteries can be charged and used many times. You do not need to replace them often.
- Regular lithium-ion batteries last for 300 to 500 cycles.
- Special batteries in electric cars last 1,000 to 2,000 cycles.
- Lithium iron phosphate batteries last over 3,000 cycles.
- More cycles mean you save money and time.
| Battery Type | Cycle Life (Cycles) |
|---|---|
| Lithium-ion | 3,000 to 5,000+ |
| Nickel-metal hydride | 500 to 800 |
| Lead-acid | 200 to 400 |
Lithium-ion batteries last longer than other types. They work better for a long time.
Fast charging
Lithium-ion batteries charge faster than most others. This helps you use your devices more.
- Phones can charge in 1 to 3 hours.
- Laptops and electric cars charge in 4 to 6 hours.
- Fast charging gives your phone 50–70% power in less than 30 minutes.
- Electric cars can reach 80% charge in 20–40 minutes.
| Device Type | Fast Charging Capability |
|---|---|
| Mobile Devices | 50–70% charge in under 30 minutes |
| Electric Vehicles | 80% charge in 20–40 minutes |
You wait less for your devices to charge. Fast charging fits your busy life and saves time.
Low self-discharge
Lithium-ion batteries lose little power when not used.
- They lose about 5% of their charge each month.
- Nickel-cadmium and nickel-metal hydride batteries lose more charge.
- Low self-discharge keeps your battery ready after storage.
Note: Low self-discharge makes lithium-ion batteries good for backup power. You can count on them to keep their charge.
Versatility
Lithium-ion batteries work in many things.
- You see them in phones, laptops, electric cars, and storage systems.
- Their high energy density and long life make them useful.
- You can use them in small gadgets or big machines.
- Cars like Tesla and Nissan Leaf use lithium-ion batteries.
| Feature | Lithium-Ion Batteries | Other Battery Chemistries |
|---|---|---|
| Versatility | Used in many different devices | Used in fewer types of devices |
| Application Examples | Phones, electric cars, energy storage | Only work in some devices |
Lithium-ion batteries are safe and flexible. They work well in many places, from daily devices to big energy systems.
Disadvantages of lithium-ion batteries

High cost
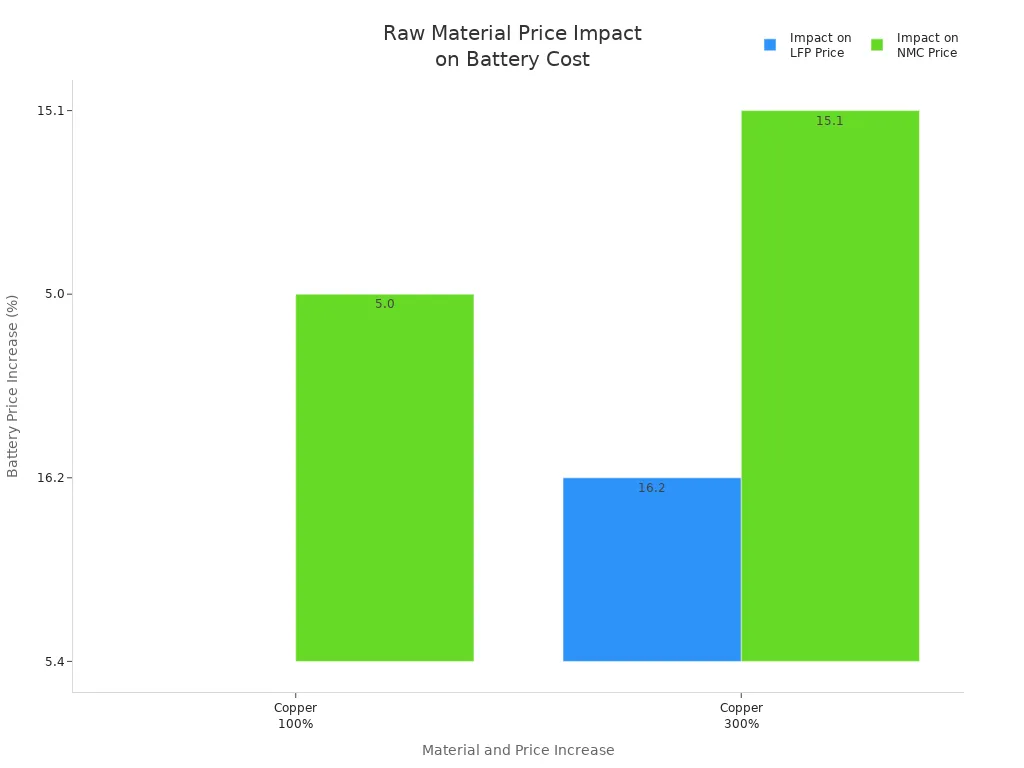
Lithium-ion batteries cost more than other batteries. The average price is $115 per kilowatt-hour in 2024. This is less than last year, but still expensive for many people. If you buy an electric car, the battery can cost from $4,760 to $19,200. In China, prices are lower at $94 per kWh. In the U.S. and Europe, prices are 31% and 48% higher.
- Making these batteries costs more because of copper, aluminum, nickel, and cobalt.
- If copper prices double, lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries cost 5.4% more.
- Nickel and cobalt prices can make nickel manganese cobalt (NMC) batteries cost over 50% more.
| Material | Price Increase | Impact on LFP Price | Impact on NMC Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | 100% | 5.4% | 5.0% |
| Copper | 300% | 16.2% | 15.1% |
| Aluminium | 400% | ~35% | N/A |
| Nickel & Cobalt | 400% | N/A | >50% |
You pay more for these batteries because of expensive materials and special ways to make them. This makes some devices and cars cost more.
Safety risks
Lithium-ion batteries can be unsafe if not handled right. Damage, wrong use, or high heat can cause fires or other dangers.
- Charging too much or using the wrong charger can make them too hot.
- Problems in making the battery can cause it to fail.
- High heat makes batteries age faster and can start fires.
| Contributing Factors | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Physical Damage | If the battery case is damaged, it can cause a fire inside. |
| Electrical Abuse | Charging too much or using too much power makes heat. This can hurt the battery and cause a fire. |
| Exposure to High Temperatures | Hot weather can break down battery parts and cause fires. |
| Manufacturing Defects | Mistakes in making the battery can make it unsafe. |
Note: In big cities, over 660 fires in six years involved these batteries. Almost 24% of electric car fires come from battery problems. In New York City, at least 12 people died from battery fires between 2021 and 2023. Over 25,000 overheating or fire cases happened in five years with products using these batteries.
You need to be careful with these batteries to stay safe. Newer batteries have better safety, but some risk is still there.
Resource limitations
Lithium-ion batteries need materials that are hard to get. Most lithium comes from Australia, Chile, and China. Getting lithium can hurt the environment by using lots of water and harming nature.
- Australia makes about 52% of the world’s lithium from rocks.
- Most cobalt comes from the Democratic Republic of Congo, which gives 70% of the world’s supply. Mining there has human rights problems.
- Getting enough lithium and cobalt is hard because of world events.
- More people want these batteries for clean energy, so prices go up and down.
- Making one tonne of lithium uses about 2 million tonnes of water. In South America, 65% of water in the lithium triangle is used for mining.
Tip: Think about how these batteries affect the earth and if they can last for the future.
Temperature sensitivity
Lithium-ion batteries work best when it is not too hot or cold. Cold weather slows them down and makes them weaker. Hot weather makes them age faster and not last as long.
- Charging works best between 0°C and 45°C (32°F to 113°F).
- Using the battery should be above -20°C (-4°F) and below 60°C (140°F).
- The best range for use is 15°C to 35°C (59°F to 95°F).
- For every 1°C rise, the battery holds 0.8% more, but too much heat is bad.
- Cold can cause lithium plating, which lowers battery power forever.
| Operation Type | Temperature Range |
|---|---|
| Charge | 0°C to 45°C (32°F to 113°F) |
| Discharge | -20°C to 60°C (-4°F to 140°F) |
| Storage | -20°C to 25°C (-4°F to 77°F) |
| Optimal Usage | 15°C to 35°C (59°F to 95°F) |
You should keep these batteries at safe temperatures to help them last longer and work well.
Maintenance needs
Lithium-ion batteries need less care than lead-acid batteries, but you still need to do some things to keep them safe and working well.
- Check batteries often for damage or rust.
- Keep them cool to stop them from getting too hot.
- Use the right charger and do not charge too much.
- Store them in a cool, dry place with 40-60% charge if not using for a long time.
- Test the battery management system often.
- Handle batteries gently to avoid damage.
- Follow the maker’s rules for care.
Note: These batteries need less care than lead-acid batteries, which need water and other steps.
These batteries are light and small, but you still need to take care of them to keep them safe and lasting longer.
Pros and cons of lithium-ion batteries in daily use
Consumer electronics
You use lithium-ion batteries in your phone and laptop. These batteries help make devices thin and light. Your gadgets are easy to carry and last longer before charging. Fast charging lets you use your device again quickly. Some devices cost more because of the battery inside. Safety problems can make you worry if you hear about battery fires. Over time, your battery may not last as long. This can make you buy new electronics more often.
| Advantage/Disadvantage | Description |
|---|---|
| High Energy Density | Lets devices be small and work well. People like smaller gadgets. |
| Fast Charging | Lets you charge quickly. People want fast charging for busy lives. |
| Cost | Higher prices can make people think before buying. This changes what people buy. |
| Safety Concerns | Safety problems can make people avoid some products. This changes what people choose. |
| Limited Lifespan | People care about how long batteries last. This changes how often they buy new devices. |
Tip: Always look for safety features when you buy new electronics.
Electric vehicles
Lithium-ion batteries power most electric cars today. You can drive far and charge quickly. These batteries last a long time, so you do not replace them often. Electric cars come in many shapes and sizes. The battery can make electric cars cost more than gas cars. If there are not enough materials, prices can go up. Safety is important because overheating can cause fires. You need to follow rules for charging and storing to stay safe.
| Pros of Lithium-Ion Batteries | Cons of Lithium-Ion Batteries |
|---|---|
| High Energy Density | Costs more than other batteries |
| Long Cycle Life | Hard to get all needed materials |
| Fast Charging | Can overheat and cause problems |
| Low Self-Discharge | |
| Variety of Sizes and Shapes |
- High energy density means you drive more miles.
- Long cycle life means you change batteries less.
- Fast charging saves you time.
- Overheating can cause fires if you do not use batteries right.
Energy storage
Lithium-ion batteries are used in home backup and big power systems. These batteries store solar and wind energy for later use. You get lots of energy in a small space. The batteries last a long time, so you do not replace them often. They work better than older batteries and lose less energy. Lithium-ion batteries are better for the environment than lead-acid batteries. You need to watch the cost and keep the batteries cool to stop overheating.
| Metric | Lithium-Ion Batteries | Lead-Acid Batteries |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | Much higher | Lower |
| Coulombic Efficiency | Very high | Lower |
| Cycle Life | Lasts much longer | Shorter life |
| Environmental Impact | Less pollution | Can cause lead problems |
- You get more power in less space.
- Longer life means fewer replacements.
- Good monitoring helps you check battery health.
- You must keep batteries cool and safe.
Note: The good and bad sides of lithium-ion batteries affect your phone, car, and even your home’s power.
Choosing a lithium ion battery
Key factors
When you pick a lithium ion battery, you should think about a few things. Each thing helps you find the best battery for what you need. Here are some important points to look at:
- Nominal voltage: Make sure the battery voltage matches your device.
- Capacity: See how much energy the battery can hold. More capacity means you can use it longer.
- Specific energy and specific power: These numbers show how much energy and power you get for the battery’s weight.
- Lifespan: Think about how many times you can charge and use the battery before it stops working well.
- Charging and discharging rates: Some batteries charge faster or give power quicker than others.
- Cost: Add up the price to buy and keep the battery working.
- Safety: Check if the battery has things to stop overheating or fires.
- Environmental impact: Pick batteries that use fewer rare materials and are easier to recycle.
Tip: Always read the battery label and user guide. This helps you use the battery safely and get the best results.
Alternatives
You might want to look at other battery types before you choose. Sodium-ion batteries are a new option for some uses. The table below shows how these two batteries are different:
| Aspect | Lithium-Ion Batteries | Sodium-Ion Batteries |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | Rare (0.0017% of Earth’s crust) | Abundant (2.6% of Earth’s crust) |
| Environmental Impact | Higher impact, more water use | Lower impact, easier recycling |
| Material Costs | $10,000 - $11,000 per ton | $600 - $650 per ton |
| Production Costs | $70 kWh | $50 kWh |
| Energy Density | 100-300 Wh/kg | 100-160 Wh/kg |
| Charging | Slower | Faster |
| Cycle Life | 8,000-10,000 cycles | 5,000 cycles |
| Safety | Flammable electrolytes | More stable chemistry |
| Weight | Lighter | Heavier |
| Material Transportation | Hazardous, higher cost | Standard, lower cost |
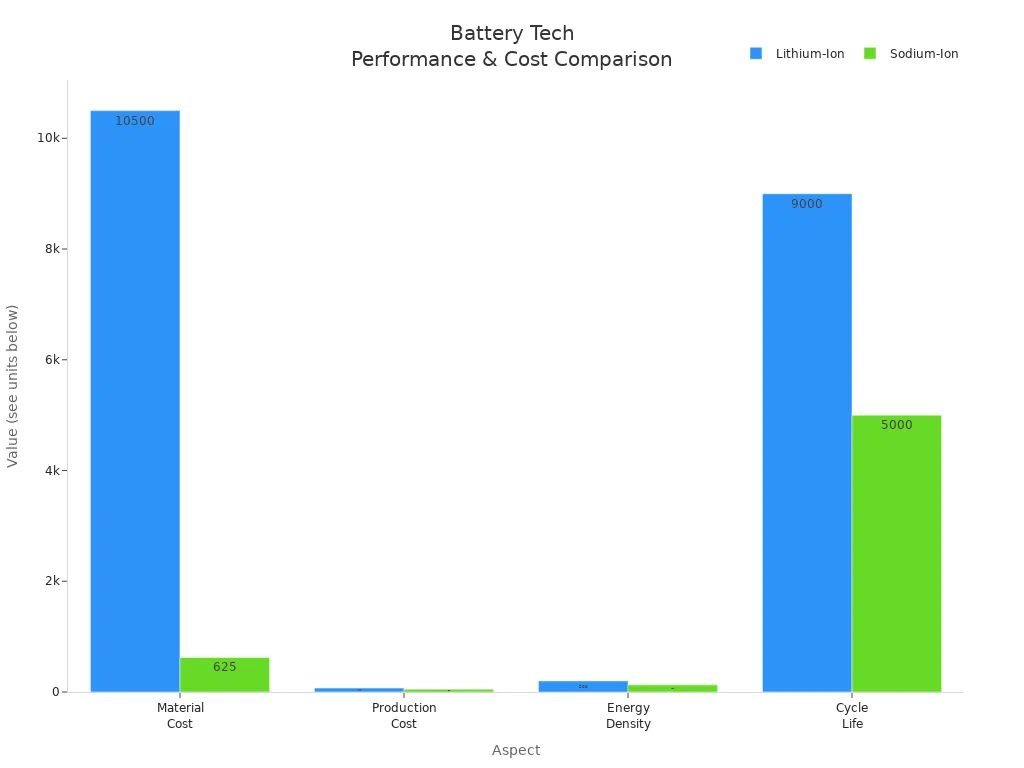
Lithium-ion batteries give you more energy and last longer. Sodium-ion batteries cost less and use safer, more common materials. You should pick the battery that fits your device, budget, and safety needs.
When picking a lithium ion battery, you should think about cost, safety, and the environment. The table below explains what is important:
| Consideration | Description |
|---|---|
| Cost | These batteries cost more at first. |
| Lifespan | They last a long time but get weaker as you use them. |
| Safety Concerns | You need to be careful when using and storing them. |
| Environmental Impact | Making and recycling them can hurt nature. |
| Temperature Sensitivity | Very hot or cold weather changes how well they work. |
Lithium ion batteries give you lots of power and last a long time. But you should also think about safety and how they affect the earth. New battery types and better recycling will help you make better choices soon.
FAQ
What devices use lithium-ion batteries?
You see lithium-ion batteries in phones, laptops, and electric cars. Solar power systems also use these batteries. Many Indian brands pick them for better use and longer life.
How do you keep lithium-ion batteries safe?
Always use the charger that comes with your device.
Keep batteries in a cool, dry spot.
Look for damage before you use them.
Never put batteries near fire or water.
Can you recycle lithium-ion batteries in India?
You can recycle lithium-ion batteries at special places. Many cities have e-waste centers. Recycling helps the earth and saves important materials.
Why do lithium-ion batteries cost more?
| Reason | Impact on Price |
|---|---|
| Rare materials | Higher production cost |
| Advanced design | More expensive to make |
You pay more because these batteries use rare metals. They also need special ways to make them.
What should you do if your battery overheats?
Take the battery out if you can do it safely. Let it cool in a safe place. Do not touch or charge it until you check for damage. If you see smoke or swelling, ask an expert for help.
-
 May.2026.02.27Lithium-Ion Batteries: The Six Constraints Blocking the Path to PerfectionLearn More
May.2026.02.27Lithium-Ion Batteries: The Six Constraints Blocking the Path to PerfectionLearn More -

 May.2026.02.25Li-Polymer Battery 5000mAh: Complete Technical & OEM GuideLearn More
May.2026.02.25Li-Polymer Battery 5000mAh: Complete Technical & OEM GuideLearn More -
 May.2026.02.24The Unparalleled Advantages of Lithium-Ion Batteries Over Traditional BatteriesLearn More
May.2026.02.24The Unparalleled Advantages of Lithium-Ion Batteries Over Traditional BatteriesLearn More -
 May.2026.02.243.6 Volt Battery: Complete Technical Guide for Engineers & BuyersLearn More
May.2026.02.243.6 Volt Battery: Complete Technical Guide for Engineers & BuyersLearn More -
 May.2026.02.24What Is a 3.8V LiPo Battery? A Complete Engineering & OEM GuideLearn More
May.2026.02.24What Is a 3.8V LiPo Battery? A Complete Engineering & OEM GuideLearn More















