What is a sodium battery and how does it work
You encounter sodium batteries as a new type of rechargeable battery that uses sodium ions to store and release energy. Unlike traditional batteries, a sodium battery relies on sodium instead of lithium, making it stand out due to the mineral’s abundance and low cost. Manufacturers see sodium batteries as a cheaper alternative to lithium batteries. The lithium-ion battery market is already worth around 50 billion dollars each year, but sodium-ion batteries have not reached a defined market size yet. As demand for energy storage rises, sodium batteries gain attention for their potential to revolutionize the field. BloombergNEF predicts that sodium-ion batteries could represent 23% of the stationary storage market by 2030, driven by their cost-effectiveness and availability. You find sodium batteries offer a promising path forward as the world seeks better ways to store renewable energy.
Key Takeaways
- Sodium batteries use sodium ions instead of lithium, making them cheaper and more abundant.
- These batteries are ideal for large-scale energy storage, especially for renewable sources like solar and wind.
- Sodium-ion batteries have a lower energy density than lithium-ion batteries but excel in safety and environmental impact.
- The technology is rapidly advancing, with commercial products expected in the near future, enhancing energy storage solutions.
- Sodium batteries can recharge quickly and are suitable for various applications, including grid storage and electric vehicles.
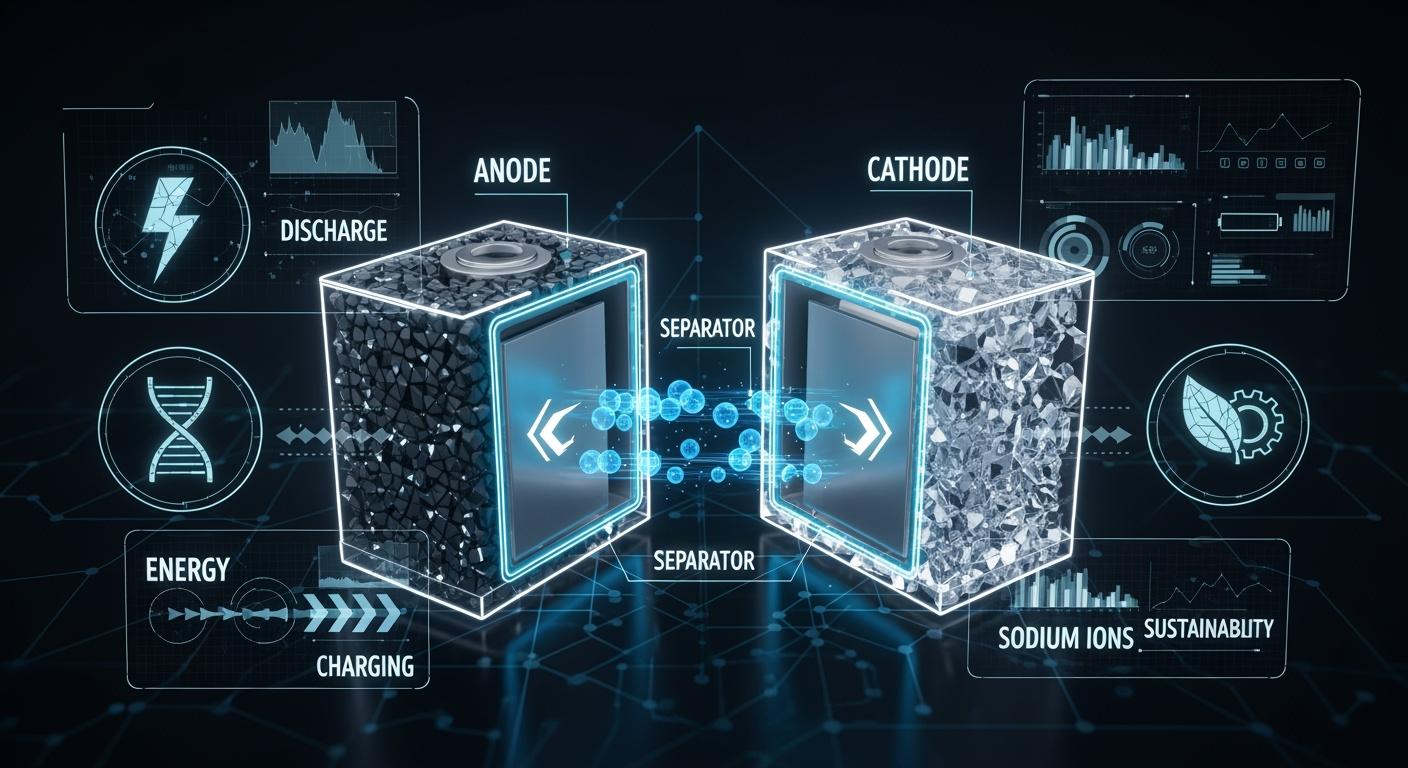
Sodium Battery Structure

Main Components
You find that a sodium battery contains several essential parts that work together to store and release energy. The main components include:
- Anode: This is the negative electrode. In sodium batteries, you often see a hard carbon material instead of the graphite used in lithium batteries. The choice of material matters because sodium ions are larger than lithium ions, so they need more space to move in and out of the anode.
- Cathode: This is the positive electrode. Manufacturers use different materials here, such as layered metal oxides or polyanionic compounds, to help sodium ions move efficiently.
- Electrolyte: This liquid or gel allows sodium ions to travel between the anode and cathode. The electrolyte must be stable and safe, supporting the movement of sodium ions without breaking down.
- Separator: This thin layer keeps the anode and cathode apart, preventing short circuits while still letting sodium ions pass through.
Tip: The structure of sodium batteries differs from lithium batteries because sodium ions are larger. This size difference means you need special electrode materials that can handle the bigger ions.
Role of Sodium Ions
Sodium ions play a central role in how these batteries work. When you charge a sodium battery, sodium ions leave the cathode and move through the electrolyte to the anode. They fit into the spaces within the anode’s carbon structure. When you use the battery to power a device, the sodium ions travel back to the cathode, releasing energy as they go.
This movement of sodium ions creates the electric current you rely on. The process is similar to what happens in lithium-ion batteries, but sodium’s larger size means the battery needs different materials and designs. You benefit from sodium’s abundance and low cost, which makes these batteries a promising choice for large-scale energy storage.
Sodium ion battery
Main Components
You encounter sodium-ion batteries as advanced energy storage devices that share many similarities with lithium-ion batteries. Both types of batteries use three main components:
- Anode: This is where sodium ions are stored during charging. Manufacturers often use hard carbon for the anode because it can accommodate the larger sodium ions.
- Cathode: This part releases sodium ions during charging and receives them during discharging. Common cathode materials include layered metal oxides and polyanionic compounds.
- Electrolyte: This liquid or gel allows sodium ions to move freely between the anode and cathode. The electrolyte must remain stable and safe throughout the battery’s operation.
A separator sits between the anode and cathode, preventing direct contact while still allowing sodium ions to pass through. You find that these components work together to enable the movement of sodium ions, which is essential for the battery’s function.
Role of Sodium ion battery
You rely on sodium-ion batteries for their ability to store and release energy efficiently. The key process involves the movement of sodium ions between the electrodes through the electrolyte. When you charge the battery, sodium ions leave the cathode and travel through the electrolyte to the anode. They settle into the anode’s structure, storing energy in the process. When you use the battery, the sodium ions move back to the cathode, releasing the stored energy as electric current. This cycle repeats every time you charge and discharge the battery.
Note: The movement of sodium ions between electrodes during charging and discharging is what makes sodium-ion batteries work. This process allows you to store energy when you have excess power and release it when you need it.
You notice that sodium-ion batteries operate on principles similar to lithium-ion batteries. Both types use ions to carry and store energy. During charging, ions move from the cathode to the anode, and during discharging, they return to the cathode. The main difference lies in the type of ion used. Sodium ions are larger and heavier than lithium ions, which affects the battery’s performance and efficiency.
- Both sodium-ion and lithium-ion batteries use ions to transfer energy.
- Sodium ions move from the cathode to the anode during charging and return during discharging, just like lithium ions.
- The chemical properties and physical size of sodium and lithium ions differ, which impacts how the batteries perform.
- Both types use an electrolyte to help ions move, creating the electric current you depend on.
You should know that sodium-ion batteries typically have a lower energy density than lithium-ion batteries. For example, current lithium-ion batteries offer energy densities between 200 and 275 Wh/kg. In comparison, some sodium-ion batteries, such as those from HiNa, reach about 145 Wh/kg. This means sodium-ion batteries may not store as much energy in the same amount of space, but they offer other important benefits.
Here is a comparison of the main advantages and disadvantages of sodium-ion batteries:
| Advantages of Sodium-Ion Batteries | Disadvantages of Sodium-Ion Batteries |
|---|---|
| Readily available | Low energy density |
| Low-cost | Short cycle-life |
| Safety | |
| Low-temperature resistance | |
| Low impact on the environment |
You benefit from sodium-ion batteries because sodium is abundant and inexpensive. These batteries also perform well in low temperatures and have a lower environmental impact. However, you may notice that they do not last as long or store as much energy as lithium-ion batteries. Despite these challenges, sodium-ion batteries continue to attract attention for large-scale energy storage and grid applications.
Sodium Batteries vs. Lithium-Ion Batteries
Design and Operation Similarities
You see that sodium batteries and lithium-ion batteries share many design and operation features. Both types of batteries use a similar structure: an anode, a cathode, an electrolyte, and a separator. You rely on these components to move ions between electrodes during charging and discharging. In both battery types, ions travel from the cathode to the anode when you charge the battery. When you use the battery, the ions move back to the cathode, creating an electric current for your devices or energy storage systems.
Both sodium batteries and lithium-ion batteries use the reactive properties of alkali metals. This similarity means you can use sodium batteries as an alternative to lithium in many applications. You benefit from the familiar operation, which makes it easier to switch to this new battery technology for energy storage needs.
Key Differences in Materials and Cost
You notice important differences between sodium batteries and lithium-ion batteries. Sodium batteries use sodium ions, which are larger and heavier than lithium ions. This size difference means sodium batteries are bigger and heavier, and they store less energy in the same space. You may find that sodium batteries have lower energy density, so they are not always the best choice for small devices.
However, sodium batteries offer a major advantage as an alternative to lithium. Sodium is much more abundant and less expensive than lithium. This abundance makes sodium batteries a cost-effective solution for large-scale energy storage. You can use sodium batteries for grid storage, renewable energy storage, and other applications where size and weight matter less than cost and availability.
Here is a quick comparison:
| Feature | Sodium Batteries | Lithium-Ion Batteries |
|---|---|---|
| Main Ion | Sodium | Lithium |
| Energy Density | Lower | Higher |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Abundance | High | Moderate |
| Best Use | Large-scale storage | Portable electronics |
Tip: If you need a battery for large-scale energy storage, sodium batteries give you a reliable and affordable alternative to lithium. You help the environment by choosing a battery technology that uses more common materials.
You see that sodium batteries are changing the way you think about energy storage. As an alternative to lithium, these batteries offer new options for battery technology and large-scale storage projects.
when will sodium ion batteries be available
You see rapid progress in sodium-ion battery technology as companies race to bring these batteries to market. Many experts predict that you will see commercial sodium-based battery products available within the next few years. Some manufacturers have already started pilot production, and you can expect wider adoption as the technology matures and costs decrease. The growing demand for affordable and sustainable energy storage drives this momentum. You may soon find sodium-ion batteries in electric vehicles, grid storage, and even consumer electronics.
Sodium Battery Manufacturers-A&S Power
You notice several companies leading the way in sodium-ion battery development. These manufacturers invest heavily in research and production to deliver reliable batteries for various applications. Some of the most notable companies include:
- Altris Ab
- Aquion Energy
- Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Ltd. (CATL)
- Faradion
- Hina Battery Technology Co. Ltd.
- BYD, which has partnered with Huahai to build a new factory for sodium-ion batteries
- Natron Energy, known for its focus on safety and durability
A&S Power also plays a significant role in the sodium-ion battery industry. You can expect these companies to shape the future of sodium-based battery solutions as they scale up production and improve performance.
Tip: Watch for announcements from these manufacturers. They often reveal new advancements and timelines for commercial availability.
How to make a sodium battery
You might wonder how to make a sodium battery. The process involves assembling several key components:
- Select an anode material, often hard carbon, to store sodium ions.
- Choose a suitable cathode, such as a layered metal oxide.
- Prepare an electrolyte that allows sodium ions to move between electrodes.
- Insert a separator to prevent short circuits.
- Assemble the battery in a controlled environment to ensure safety and performance.
You should know that manufacturing sodium-ion batteries requires specialized equipment and strict quality control. Most consumers cannot build these batteries at home, but you benefit from the expertise of leading manufacturers who ensure each battery meets industry standards.
Applications and Future of Sodium Batteries
Current Uses
You see sodium batteries making a strong impact in energy storage today. Companies like CATL and BYD invest billions to develop sodium batteries as a more affordable and sustainable alternative to lithium-based batteries. BYD is building a gigafactory with a 30 GWh annual capacity, aiming to make energy storage accessible for everyone. You find sodium batteries used in energy storage systems that support wind and solar power, helping stabilize the grid and store renewable energy for later use.
- Sodium batteries are being developed for specific market niches, especially for energy storage in wind and solar energy.
- You notice that sodium-ion battery applications are expanding as researchers at MIT create new sodium batteries with all-organic cathodes. These batteries use basic elements like carbon and oxygen, which could match lithium battery performance at a lower cost and reduce reliance on rare metals.
The Baochi Energy Storage Station in China stands as a major example. This facility, opened in May 2025, combines lithium-ion and sodium-ion batteries with a total capacity of 400 megawatt-hours. It stores and releases enough energy to power about 270 homes each year. Most of the stored energy comes from local solar and wind farms, showing how sodium batteries support energy storage and grid stability.
Future Outlook
You can expect sodium batteries to play an even bigger role in energy storage systems over the next decade. New advancements promise to improve performance, lower costs, and increase sustainability. For example:
- The latest sodium battery technology could lead to electric cars priced under $25,000.
- Production costs will drop as manufacturers use more abundant materials.
- Some new batteries can recharge in just 11 minutes, making them practical for daily use.
| Advancement | Description |
|---|---|
| New Material | CINE researchers developed a material that boosts sodium battery performance. |
| Ion Insertion Speed | Faster sodium ion movement increases charge storage and efficiency. |
| Sustainability | Sodium’s abundance makes these batteries more sustainable and affordable. |
You will see sodium batteries improve energy storage by solving the intermittency problems of solar and wind power. Their increased capacity and durability will help you store energy during peak production and use it when needed. As sodium batteries offer low impact on the environment and support sustainability, you will find them essential for the future of renewable energy and large-scale storage. Their low impact on the environment and cost advantages make them a smart choice for the next generation of energy storage solutions.
You now understand that sodium batteries offer a promising solution for energy storage.
- Sodium-ion batteries use abundant sodium, making them more accessible than lithium options.
- These batteries perform well in extreme temperatures and maintain high efficiency over many cycles.
- Large-scale systems, such as the 100 MWh installation, show their scalability.
| Study | Focus Area |
|---|---|
| Fernández-Ropero et al. (2018) | Low-cost cathodes |
| Han et al. (2018, 2020) | Advanced electrolytes |
| Zhang et al. (2022) | All-climate performance |
Stay informed about new breakthroughs in sodium-ion battery technology. You could soon see these batteries transform how you store and use energy.
-
 May.2026.02.27Lithium-Ion Batteries: The Six Constraints Blocking the Path to PerfectionLearn More
May.2026.02.27Lithium-Ion Batteries: The Six Constraints Blocking the Path to PerfectionLearn More -

 May.2026.02.25Li-Polymer Battery 5000mAh: Complete Technical & OEM GuideLearn More
May.2026.02.25Li-Polymer Battery 5000mAh: Complete Technical & OEM GuideLearn More -
 May.2026.02.24The Unparalleled Advantages of Lithium-Ion Batteries Over Traditional BatteriesLearn More
May.2026.02.24The Unparalleled Advantages of Lithium-Ion Batteries Over Traditional BatteriesLearn More -
 May.2026.02.243.6 Volt Battery: Complete Technical Guide for Engineers & BuyersLearn More
May.2026.02.243.6 Volt Battery: Complete Technical Guide for Engineers & BuyersLearn More -
 May.2026.02.24What Is a 3.8V LiPo Battery? A Complete Engineering & OEM GuideLearn More
May.2026.02.24What Is a 3.8V LiPo Battery? A Complete Engineering & OEM GuideLearn More