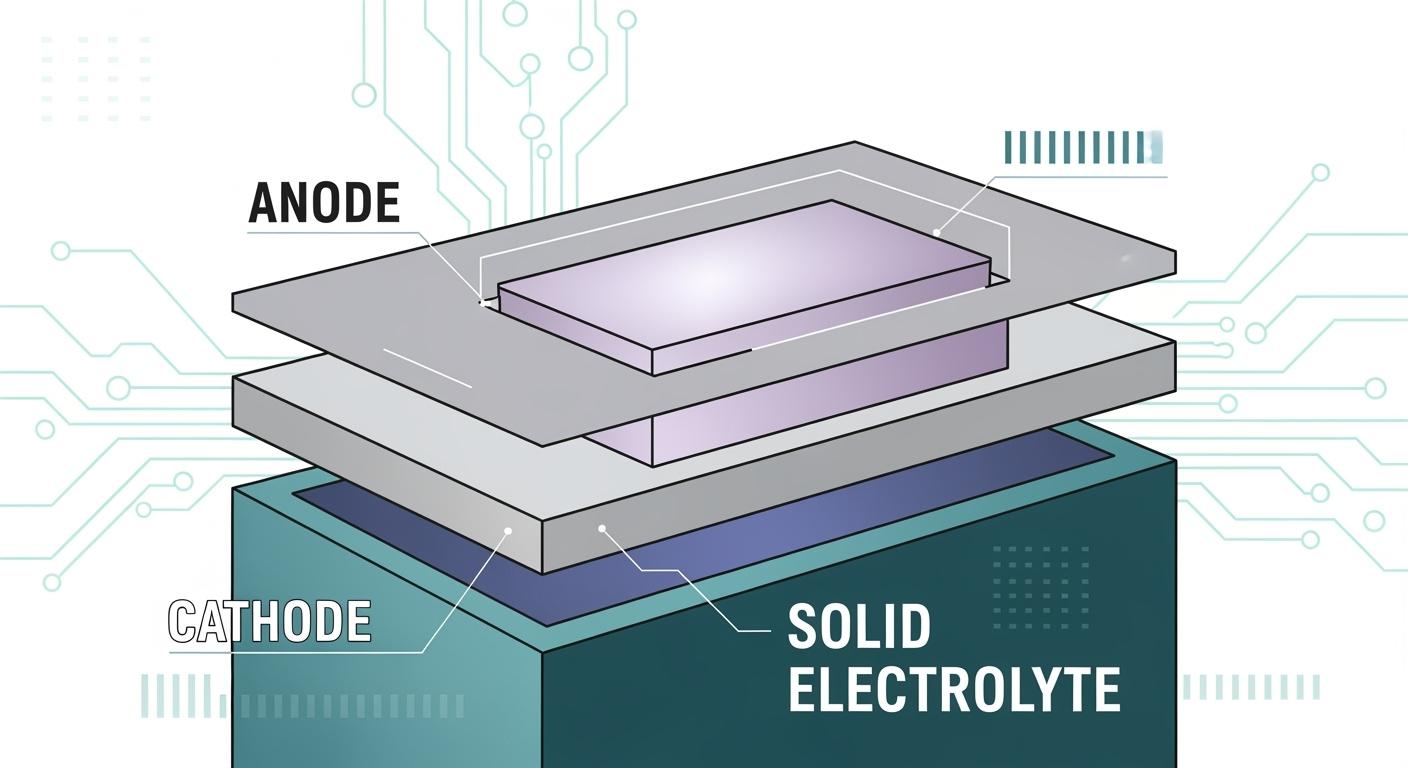
What Is an All-Solid-State Battery Cell
You might wonder how all-solid-state batteries are different from lithium-ion cells in most devices. These new batteries use a solid electrolyte, not a liquid one. Solid state batteries are safer and more reliable. The chance of leaks or fires is much lower. They also have higher energy density. This means you could drive about 600 miles before charging again. Charging is much faster too. You can get to 80% charge in only nine minutes. The first all-solid-state battery cells show how this technology can change electric vehicles and portable electronics.
Key Takeaways
- All-solid-state batteries use solid electrolytes. This makes them safer. They are less likely to leak. They are also less likely to catch fire.
- These batteries charge very fast. They can reach 80% in just nine minutes. This helps people use their devices more easily.
- Solid-state batteries last a long time. They can work for over 10,000 cycles. Traditional lithium-ion batteries last only 1,000 to 2,000 cycles.
- Solid-state batteries have higher energy density. This means devices can run longer before charging again. This makes using them better for people.
- As technology gets better, the cost will go down. Solid-state batteries will become cheaper. More people will be able to use them every day.
Battery Structure and Operation

Solid Electrolyte Function
The solid electrolyte is very important in all-solid-state batteries. It takes the place of the liquid or gel electrolyte in older batteries. The solid electrolyte lets ions move between the positive and negative electrodes. This makes the battery safer because there are no leaks or fires. Solid electrolytes also help stop dendrites from growing. Dendrites can cause short circuits in other batteries.
You can look at the table below to see how battery types are different:
| Feature | All-Solid-State Batteries | Traditional Lithium-Ion Batteries |
|---|---|---|
| Electrolyte Type | Solid electrolyte | Liquid or gel electrolyte |
| Design | All components are solid | Contains porous separator and liquid electrolyte |
| Energy Density | Higher potential energy density | Lower energy density compared to SSBs |
| Safety | More stable, less flammable | Flammable liquid electrolyte |
| Thickness | Can be thinner due to compact design | Bulkier due to separator and excess electrolyte |
Solid state batteries use different kinds of solid electrolytes. Sulfide-based electrolytes let ions move very well, but they need to be more stable. Oxide-based electrolytes are very stable, but ions do not move as quickly.
Tip: Solid electrolytes help make batteries safer and more reliable. This is good for devices you use every day.
Key Components
All-solid-state batteries have three main parts:
- Positive Electrode (Cathode): This part stores energy and helps the battery give power.
- Negative Electrode (Anode): This part holds the charge and helps the battery release energy.
- Solid Electrolyte: This layer sits between the electrodes. It lets ions move and keeps the battery safe from leaks.
These parts work together to give high energy and strong performance. Solid state batteries use solid electrolytes to lower the risk of leaks. You can trust these batteries in important devices, like cardiac pacemakers, because they are safe and reliable.
The type of solid electrolyte changes how well the battery works. Sulfide-based types move ions fast but need better stability. Oxide-based types are very stable but need to move ions faster.
How Solid State Batteries Work
You can see how all-solid-state batteries work by looking at ion movement. When you charge the battery, ions go from the positive electrode to the negative electrode through the solid electrolyte. When you use the battery, ions move back and make an electric current. This current powers your device.
Solid state batteries use solid electrolytes instead of flammable liquids. This makes them safer and more stable. Liquid electrolytes can break down at high voltages and cause battery problems. Solid electrolytes can handle higher voltages, so you get better performance.
Here is a table that compares ionic conductivity:
| Type of Electrolyte | Ionic Conductivity (S cm−1) | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liquid Electrolytes | 10−2 to 10−3 | Good conductivity | Stability issues, leakage, dendrite growth |
| Solid Electrolytes | Generally lower | Safety, stability, suppress dendrite growth | Low room temperature conductivity, limits practical use |
Solid state batteries have lower ionic conductivity at room temperature. This means they may not charge as fast as liquid batteries sometimes. But you get much better safety and stability.
Note: All-solid-state batteries will become more common as scientists make ion movement faster in solid electrolytes.
If you want batteries that last longer, charge quickly, and keep you safe, solid state batteries are a good choice.
Comparing Solid-State Battery Technology
Material Differences
There are clear differences in the materials used. Solid state batteries use solid electrolytes like sulfide-based types. These help stop leaks and fires. Conventional batteries use liquid electrolytes. These can catch fire. Solid state batteries use carbon nanofibres as additives. Traditional batteries use spherical carbon. The table below shows these differences:
| Material Type | All-Solid-State Batteries (ASSBs) | Conventional Lithium-Ion Batteries |
|---|---|---|
| Electrolyte | Sulfide-based solid electrolytes | Liquid electrolytes |
| Conductive Additives | Carbon nanofibres (CNFs) | Spherical carbon (SC) |
| Safety | Nonflammable | Flammable |
| Performance | High energy and power density | Moderate energy and power density |
These advanced materials make solid state batteries safer and better.
Safety and Performance
All-solid-state batteries are much safer. They do not catch fire or explode, even in tough tests. For example:
Tests at University College London show Goliath prototypes do not explode or catch fire. This happens even when lithium-ion cells would fail. In a nail test, Goliath P1 cells stayed safe. Their outside temperature stayed below 80°C. Lithium-ion batteries often get very hot and dangerous.
Solid state batteries last much longer. They can work for over 10,000 cycles and keep 90% of their power. Conventional lithium-ion batteries last for 1,000 to 2,000 cycles with 80% power left. The table below compares their performance:
| Battery Technology | Cycle Life | Capacity Retention | Years of Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium-ion | 1,000-2,000 | 80% | 3-5 years |
| Solid State | 10,000+ | 90% | 15-20 years |
Energy Density
All-solid-state batteries store more energy. They fit more power in a smaller space. For example, Ilika’s solid state batteries reach 350 Wh/kg. Conventional lithium-ion batteries reach only 293 Wh/kg. The table below shows this difference:
| Battery Type | Energy Density (Wh/kg) |
|---|---|
| Conventional Lithium-Ion | 293 |
| Solid-State Battery (Ilika) | 350 |
Solid state batteries let you use devices longer between charges. They also make devices lighter and more efficient. This is why all-solid-state batteries are becoming the top choice for future technology.
Advantages and Challenges of All-Solid-State Batteries
Safety Improvements
All-solid-state batteries are much safer than older batteries. They use solid electrolytes, so there are no leaks or fires. You do not need to worry about explosions or overheating. These batteries work well in tough conditions. They stop dangerous dendrite growth. Dendrites can cause short circuits in other batteries. You can trust devices with these batteries, even in hard places.
Tip: If you need a battery for medical devices or electric vehicles, solid state batteries are a safe choice. You avoid problems that come with liquid electrolytes.
Performance Benefits
Solid state batteries work very well. They last longer and charge faster. These batteries can be used thousands of times and keep most of their power. You do not wait long for your device to charge. They have higher energy density, so your phone or car works longer before charging.
| Feature | Solid State Batteries | Conventional Batteries |
|---|---|---|
| Cycle Life | 10,000+ cycles | 1,000-2,000 cycles |
| Energy Density | Up to 350 Wh/kg | Up to 293 Wh/kg |
| Charging Speed | Rapid | Moderate |
You will see the difference every day. Devices last longer and charge quickly. These batteries work well in hot or cold weather. They do not lose power in cold weather as fast as older batteries.
Cost and Manufacturing
You might think about the cost of solid state batteries. At first, they cost more to make than lithium-ion batteries. Manufacturers need new machines and must work with car companies. Most of the process is like making lithium-ion batteries. This helps keep costs lower.
- Solid state batteries get cheaper as more are made.
- New battery types cost a lot at first, but prices drop when factories make more.
- Lighter batteries can cut the cost of electric vehicles by up to 50%.
Making these batteries is not easy. They need new materials and careful building. There are problems like high resistance and keeping the battery strong. Some solid electrolytes break easily, so making lots of batteries is hard. Power conductivity needs to get better, especially in cold weather.
- High resistance between parts can slow charging.
- Some solid materials break, which causes problems.
- Making lots of batteries is still hard for companies.
- Side reactions can lower battery life and power.
Note: Costs will go down and performance will get better as scientists fix these problems. Manufacturers are working to make all-solid-state batteries better and easier to build.
You will see more all-solid-state batteries as technology improves. You will get safer, longer-lasting, and better devices in the future.
First All-Solid-State Battery Cells and Industry Progress
Industry Innovations
The first all-solid-state battery cells have changed the battery industry. Many companies and research teams have worked together to reach big goals. The table below lists some important achievements:
| Milestone | Date | Organisation(s) Involved |
|---|---|---|
| Material Development | July 2020 | Schott, Umicore, Hydro Quebec, Abee, CIC energiGUNE |
| First Batch of Cells | N/A | CIC energiGUNE (led consortium) |
Working together has helped a lot. BMW and Solid Power started working together in 2016. They made their partnership stronger in 2022. The i7 test car showed how these batteries can power electric cars. These steps show how quickly the technology is improving.
Many companies are making new ideas. Coros Battery in South Korea made glass fibre separators with solid electrolytes. One Energetics in the USA found ways to charge many batteries at once. Phoenix Battery in Taiwan made a solid Li-ion battery with a special cathode. Quantum Generative Materials uses machine learning to predict how ions move in solid electrolytes. Torow in France leads a project to reach 430 Wh/kg energy density by 2028. These examples show that the first all-solid-state battery cells are getting better and safer.
Recent progress in all-solid-state batteries is about making them safer, stronger, and easier to build. You will see more improvements soon.
Scalability and Future Potential
You might ask if these batteries can be made for everyone. Ilika’s Goliath programme is working on this. They want to use solid state batteries in cars and electronics. Ilika works with car makers like JLR, McLaren, and Honda. They use machines from the lithium-ion industry to make batteries faster. Ilika has also received £24.7 million to help build a big factory.
The Goliath programme made ten times more batteries in 2023 than before. They focus on making batteries that last longer and are safer for electric cars. The Faraday Institution’s SOLBAT project helps by studying how the parts of solid state battery cells work together.
The market for these batteries is growing fast. Experts say it could grow from USD 1.14 billion in 2024 to USD 56.05 billion by 2035. Asia Pacific leads in making electric cars, with help from governments in China, Japan, and South Korea. North America and Europe are also making progress with new projects and help from car companies.
You will see these batteries in more devices soon. Companies like Toyota, Panasonic, Samsung, and Solid Power are already making test batteries. These efforts show that solid state battery technology is ready for the future. You can look forward to safer, longer-lasting, and stronger batteries in your daily life.
Solid state batteries have special features. They use solid electrolytes that do not catch fire. They also hold more energy than other batteries. These batteries are safer than lithium-ion batteries. They charge faster and last longer. The table below shows how they are different:
| Aspect | Lithium-Ion Battery | Solid State Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Safety | Flammable | Non-flammable |
| Energy Density | Moderate | High |
| Charging Speed | Standard | Rapid |
Solid state batteries will change electric cars and energy storage. You will get safer devices and better power. If you want to know more, you can email us or use our contact form.
-
 May.2026.02.27Lithium-Ion Batteries: The Six Constraints Blocking the Path to PerfectionLearn More
May.2026.02.27Lithium-Ion Batteries: The Six Constraints Blocking the Path to PerfectionLearn More -

 May.2026.02.25Li-Polymer Battery 5000mAh: Complete Technical & OEM GuideLearn More
May.2026.02.25Li-Polymer Battery 5000mAh: Complete Technical & OEM GuideLearn More -
 May.2026.02.24The Unparalleled Advantages of Lithium-Ion Batteries Over Traditional BatteriesLearn More
May.2026.02.24The Unparalleled Advantages of Lithium-Ion Batteries Over Traditional BatteriesLearn More -
 May.2026.02.243.6 Volt Battery: Complete Technical Guide for Engineers & BuyersLearn More
May.2026.02.243.6 Volt Battery: Complete Technical Guide for Engineers & BuyersLearn More -
 May.2026.02.24What Is a 3.8V LiPo Battery? A Complete Engineering & OEM GuideLearn More
May.2026.02.24What Is a 3.8V LiPo Battery? A Complete Engineering & OEM GuideLearn More